S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E
Hi students, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMB). In this post, you will get S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E. This is the chapter of introduction of ‘Quadratic Equations‘ included in ICSE 2020 Class 10 Maths syllabus.
In S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E, word problems are given. First, we need to make a quadratic equation according to the given question and then we need to solve them.
Read : Quadratic Equations Class 10 ICSE Maths Notes PDF
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 1
The sum of the squares of two consecutive positive even integers is 100. Find the integers.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let two consecutive positive even integers are x and (x + 2). Then, we have
x2 + (x + 2)2 = 100
⇒ x2 + x2 + 4x + 4 = 100
⇒ 2x2 + 4x – 96 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2x – 48 = 0
⇒ x2 + 8x – 6x – 48 = 0
⇒ x(x + 8) – 6(x + 8) = 0
⇒ (x – 6)(x + 8) = 0
⇒ x = 6 or -8
Since x is positive even integer, then x = 6 and hence other positive even integer is (x + 2) = 8.
Thus, the required integers are 6 and 8.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 2
Find two rational numbers which differ by 3 and the sum of whose squares is 117.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let two rational numbers are x and (x + 3). Then, we have
x2 + (x + 3)2 = 117
⇒ x2 + x2 + 6x + 9 = 117
⇒ 2x2 + 6x + 9 = 117
⇒ 2x2 + 6x – 108 = 0
⇒ x2 + 3x – 54 = 0
⇒ x2 + 9x – 6x – 54 = 0
⇒ x(x + 9) – 6(x + 9) = 0
⇒ (x – 6)(x + 9) = 0
⇒ x = 6 or -9
If x = 6, then (x + 3) = 9
If x = -9, then (x + 3) = -6
Thus, the required rational numbers are 6 and 9 or -9 and -6.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 3
What number increased by its reciprocal equals 65/8?
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the number is x. Then, we have
x + 1/x = 65/8
⇒ (x2 + 1)/x = 65/8
⇒ 8(x2 + 1) = 65x
⇒ 8x2 – 65x + 8 = 0
⇒ 8x2 – 64x – x + 8 = 0
⇒ 8x(x – 8) – 1(x – 8) = 0
⇒ (8x – 1)(x – 8) = 0
⇒ x = 1/8 or 8
Thus, the required number is 8 or 1/8.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 4
The sum of the numerator and denominator of a certain fraction is 8. If 2 is added to the numerator and to the denominator, the value of the fraction is increased by 4/35. Find the fraction.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the fraction is x / (8 – x). Then, we have
(x + 2)/(8 – x + 2) = x/(8 – x) + 4/35
⇒ (x + 2)/(10 – x) – x/(8 – x) = 4/35
⇒ [(x + 2)(8 – x) – x(10 – x)]/(10 – x)(8 – x) = 4/35
⇒ [8x – x2 + 16 – 2x – 10x + x2]/(80 – 10x – 8x + x2) = 4/35
⇒ 35[16 – 4x] = 4(x2 – 18x + 80)
⇒ 35[4 – x] = (x2 – 18x + 80)
⇒ x2 + 17x – 60 = 0
⇒ x2 + 20x – 3x – 60 = 0
⇒ x(x + 20) – 3(x + 20) = 0
⇒ (x – 3)(x + 20) = 0
⇒ x = 3 or -20
Thus, the required fraction is x/(8 – x) = 3/5.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 5
There are three consecutive integers such that the square of the first increased by the product of the other two gives 154. Find the integers.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let three consecutive integers are x, (x + 1) and (x + 2). Then, we have
x2 + (x + 1)(x + 2) = 154
⇒ x2 + x2 + 3x + 2 = 154
⇒ 2x2 + 3x – 152 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 16x + 19x – 152 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 8) + 19(x – 8) = 0
⇒ (2x + 19)(x – 8) = 0
⇒ x = -19/2 or 8.
Thus, the required three consecutive integers are 8, 9, 10.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 6
The sum of two numbers is 8 and 15 times the sum of their reciprocals is also 8. Find the numbers.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let two numbers are x and (8 – x). Then, we have
15[1/x + 1/(8 – x)] = 8
⇒ 15(8 – x + x)/x(8 – x) = 8
⇒ 15(8) = 8x(8 – x)
⇒ 15 = x(8 – x)
⇒ x2 – 8x + 15 = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x – 5x + 15 = 0
⇒ x(x – 3) – 5(x – 3) = 0
⇒ (x – 5)(x – 3) = 0
⇒ x = 3 or 5
If x = 3, then (8 – x) = 5
If x = 5, then (8 – x) = 3
Thus, the required numbers are 3 and 5.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 7
A two digit number is such that the product of the digits is 12. When 36 is added to this number, the digits interchange their places. Find the number.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the unit digit of the number is x, then its tens digit is 12/x. Then, we have
10(12/x) + x + 36 = 10x + 12/x
⇒ 9x – 9(12/x) = 36
⇒ x – (12/x) = 4
⇒ (x2 – 12)/x = 4
⇒ (x2 – 12) = 4x
⇒ x2 – 4x – 12 = 0
⇒ x2 – 6x + 2x – 12 = 0
⇒ x(x – 6) + 2(x – 6) = 0
⇒ (x + 2)(x – 6) = 0
⇒ x = -2 or 6
Since x is a digit, then x = 6.
Thus, the unit digit is x = 6 and tens digit 12/x = 2 and hence the number is 26
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 8
Five times a certain whole number is equal to three less than twice the square of the number. Find the number.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the whole number is x. Then, we have
5x = 2x2 – 3
⇒ 2x2 – 5x – 3 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 6x + x – 3 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 3) + 1(x – 3) = 0
⇒ (2x + 1)(x – 3) = 0
⇒ x = -1/2 or 3
Since x is a whole number, then the required number is x = 3.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 9
Three consecutive numbers are such that the square of the middle number exceeds the difference of the squares of the other two by 60. Assume the middle number to be x and form a quadratic equation satisfying the above statement. Hence, find the three numbers.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the three number are (x – 1), x, (x + 1). Then, we have
x2 = (x + 1)2 – (x – 1)2 + 60
⇒ x2 = x2 + 2x + 1 – x2 + 2x – 1 + 60
⇒ x2 – 4x – 60 = 0
⇒ x2 – 10x + 6x – 60 = 0
⇒ x(x – 10) + 6(x – 10) = 0
⇒ (x + 6)(x – 10) = 0
⇒ x = -6 or 10
Thus, the three numbers are 9, 10 and 11.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 10
The sum of the ages (in years) of a son and his father is 35 and the product of their ages is 150. Find their ages.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the father’s age is x years then his son’s age is (35 – x) years. Then, we have
x(35 – x) = 150
⇒ 35x – x2 = 150
⇒ x2 – 35x + 150 = 0
⇒ x2 – 30x – 5x + 150 = 0
⇒ x(x – 30) – 5(x – 30) = 0
⇒ (x – 5)(x – 30) = 0
⇒ x = 5 or 30
Thus, the father’s age is x = 30 years then his son’s age is (35 – x) = 5 years
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 11
Anjali was born in 1985 A.D. In the year x2 AD, she was (x – 5) years old. Find the value of x.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
In the year x2 AD, Anjali was (x – 5) years old. Then, we have
x2 – 1985 = (x – 5)
⇒ x2 – x – 1980 = 0
⇒ x2 – 45x + 44x – 1980 = 0
⇒ x(x – 45) + 44(x – 45) = 0
⇒ (x + 44)(x – 45) = 0
⇒ x = -44 or 45
Since x is year, x = 45.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 12
The difference of mother’s age and her daughter’s age is 21 years and the twelfth part of the product of their ages is less than the mother’s age by 18 years. Find their ages.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the daughter’s age is x years then her mother’s age is (x + 21) years. Then, we have
x(x + 21) / 12 = (x + 21) – 18
⇒ x2 + 21x = 12(x + 3)
⇒ x2 + 21x = 12x + 36
⇒ x2 + 9x – 36 = 0
⇒ x2 + 12x – 3x – 36 = 0
⇒ (x + 12) – 3(x + 12) = 0
⇒ (x – 3)(x + 12) = 0
⇒ x = 3 or -12
Since x is an age, x = 3
Thus, daughter’s age is x = 3 years and mother’s age is (x + 21) = 24 years.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 13
Reena is x year old, while her father Mr. Sunil is x2 years old. 5 years hence, Mr Sunil will be three times as old as Reena. Find their present ages.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Given that Reena is x year old, while her father Mr. Sunil is x2 years old.
After 5 years, Mr Sunil will be three times as old as Reena.
Then, we have
x2 + 5 = 3(x + 5)
⇒ x2 – 3x – 10 = 0
⇒ x2 – 5x + 2x – 10 = 0
⇒ x(x – 5) + 2(x – 5) = 0
⇒ (x + 2)(x – 5) = 0
⇒ x = -2 or 5
Since x is an age, x = 5.
Thus, Reena is x = 5 year old and her father Mr. Sunil is x2 = 25 years old.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 14
Form a quadratic equation from the following information, taking as width x ∈ N.
(i) The area of rectangle whose length is five more than twice its width is 75.
(ii) Solve the equation and find its length.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Given that the width of rectangle is x, and hence the length of the rectangle is (2x + 5).
Then, we have
x(2x + 5) = 75
⇒ 2x2 + 5x – 75 = 0 [This is required quadratic equation.]
⇒ 2x2 + 15x – 10x – 75 = 0
⇒ x(2x + 15) – 5(2x + 15) = 0
⇒ (x – 5)(2x + 15) = 0
⇒ x = 5 or -15/2
Thus, the width of the rectangle is x = 5.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 15
The sides of a right angled triangle containing the right angle are 5x cm and (3x – 1) cm. If the area of the triangle be 60 cm2, calculate the lengths of the sides of triangle.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Given that the area of a right angled triangle, whose legs are 5x cm and (3x – 1) cm, is 60 cm2.
Then, we have
(1/2) × (5x) × (3x – 1) = 60
⇒ 15x2 – 5x – 120 = 0
⇒ 5(3x2 – x – 24) = 0
⇒ 3x2 – x – 24 = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 9x + 8x – 24 = 0
⇒ 3x(x – 3) + 8(x – 3) = 0
⇒ (3x + 8)(x – 3) = 0
⇒ x = 3 or -8/3
Thus, the legs of the right angled triangle are 5x = 15 and (3x – 1) = 8 and hence its hypotenuse is √(82 + 152) = 17.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 16
The hypotenuse of a right angle triangle is 13 cm and the difference between the other two sides is 7 cm.
(i) Taking x as the length of the shorter of the two sides, write an equation in x that represents the above statement.
(ii) Solve the equation obtained in (i) above and hence find the two unknowns sides of the triangle.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the length of legs of right angled triangle are x and (x + 7). Then, we have
x2 + (x + 7)2 = 132
⇒ x2 + x2 + 14x + 49 = 169
⇒ 2x2 + 14x – 120 = 0
⇒ x2 + 7x – 60 = 0 [This is required quadratic equation.]
⇒ x2 + 12x – 5x – 60 = 0
⇒ x(x + 12) – 5(x + 12) = 0
⇒ (x – 5)(x + 12) = 0
⇒ x = 5 or -12
Thus, the two legs of the right angled triangle are x = 5 and (x + 7) = 12.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 17
The length of a verandah is 3 m more than its breadth. The numerical value of its area is equal to the numerical value of its perimeter.
(i) Taking x as the breadth of the verandah, write an equation in x that represents the above statement.
(ii) Solve the equation in (i) above and hence find the dimension of the verandah.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the dimension of the verandah are x and (x + 3). Then, we have
x(x + 3) = 2(x + x + 3)
⇒ x2 + 3x = 4x + 6
⇒ x2 – x – 6 = 0 [This is required quadratic equation.]
⇒ x2 – 3x + 2x – 6 = 0
⇒ x(x – 3) + 2(x – 3) = 0
⇒ (x + 2)(x – 3) = 0
⇒ x = 3 or -2.
Thus, the dimension of the verandah are width as x = 3 and length as (x + 3) = 6.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 18
Two squares have sides x cm and (x + 4) cm. The sum of their areas is 656 sq cm. Express this as an algebraic equation in x and solve the equation to find sides of the squares.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Two squares have sides x cm and (x + 4) cm. Then, we have
x2 + (x + 4)2 = 656
⇒ x2 + x2 + 8x + 16 = 656
⇒ 2x2 + 8x – 640 = 0
⇒ x2 + 4x – 320 = 0 [This is required quadratic equation.]
⇒ x2 – 16x + 20x – 320 = 0
⇒ x(x – 16) + 20(x – 16) = 0
⇒ (x + 20)(x – 16) = 0
⇒ x = -20 or 16
Since x represents the length of the side of square, then x = 16.
Thus, the sides of the squares are 16 cm and 20 cm.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 19
The perimeter of a rectangular plot is 180 m and its area is 1800 cm2. Take the length of plot as x m. Use the perimeter 180 m to write the value of the breadth in terms of x. Use the values of length, breadth and the area to write an equation in x. Solve the equation to calculate the length and breadth of the plot.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Given that the length of rectangular plot is x m. Then, we have
2(length + breadth) = 180
⇒ 2(x + breadth) = 180
⇒ breadth = 90 – x.
Now, Area = 1800
⇒ x(90 – x) = 1800
⇒ 90x – x2 = 1800
⇒ x2 – 90x + 1800 = 0
⇒ x2 – 60x – 30x + 1800 = 0
⇒ x(x – 60) – 30(x – 60) = 0
⇒ (x – 30)(x – 60) = 0
⇒ x = 30 or 60.
If x = 30, then 90 – x = 60
If x = 60, then 90 – x = 30
Thus, length = 60 cm and width = 30 cm
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 20
A rectangle has an area of 24 cm2. If its length is x cm, write down its breadth in terms of x. Given that its perimeter is 20 cm, form an equation in x and solve it.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Given that the length of rectangle is x m. Then, we have
length * breadth = 24
⇒ x * breadth = 24
⇒ breadth = 24/x.
Now, Perimeter = 20
⇒ 2(x + 24/x) = 20
⇒ (x + 24/x) = 10
⇒ x2 + 24 = 10x
⇒ x2 – 10x + 24 = 0
⇒ x2 – 6x – 4x + 24 = 0
⇒ x(x – 6) – 4(x – 6) = 0
⇒ (x – 4)(x – 6) = 0
⇒ x = 4 or 6
Since x is length of the rectangle, then x = 6 and 24/x = 4.
Thus, length and breadth of the rectangle are 6 cm and 4 cm.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 21
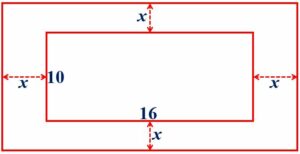
A rectangular garden 10 m by 16 m is to be surrounded by a concrete path of uniform width. Given that the area of the path is 120 squares meters, assuming the width of the path to be x, form an equation in x and solve it to find the value of x.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Given that the width of the wall to be x. Then, we have
(2x + 16)(2x + 10) – 10 × 16 = 120
⇒ 4x2 + 52x + 160 – 160 = 120
⇒ 4x2 + 52x – 120 = 0
⇒ x2 + 13x – 30 = 0
⇒ x2 + 15x – 2x – 30 = 0
⇒ x(x + 15) – 2(x + 15) = 0
⇒ (x – 2)(x + 15) = 0
⇒ x = 2 or -15
Thus, the width of the path is x = 2 cm.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 22
A man covers a distance of 200 km travelling with a uniform speed of x km per hour. The distance could have been covered in 2 hours less, had the speed been (x + 5)km/he. Calculate the value of x.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
According to question, we have
200/x – 200/(x + 5) = 2
⇒ 1/x – 1/(x + 5) = 1/100
⇒ (x + 5 – x)/x(x + 5) = 1/100
⇒ 5/x(x + 5) = 1/100
⇒ x2 + 5x – 500 = 0
⇒ x2 + 25x – 20x – 500 = 0
⇒ x(x + 25) – 20(x + 25) = 0
⇒ (x – 20)(x + 25) = 0
⇒ x = 20 or -25.
Thus, required speed is x = 20 km/hr.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 23
An express train makes a run of 240 km at a certain speed. Another train, whose speed is 12 km/hr less than the first takes an hour longer to make the same trip. Find the speed of the express train to km/hr.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the speed of the express train is x km/hr, we have
240/(x – 12) – 240/x = 1
⇒ 1/(x – 12) – 1/x = 1/240
⇒ (x – x + 12)/x(x – 12) = 1/240
⇒ 12/x(x – 12) = 1/240
⇒ x2 – 12x – 2880 = 0
⇒ x2 – 60x + 48x – 2880 = 0
⇒ x(x – 60) + 48(x – 60) = 0
⇒ (x + 48)(x – 60) = 0
⇒ x = -48 or 60
Thus, the speed of the express train is 60 km/hr.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 24
A train covers a distance of 90 km at a uniform speed. Had the speed been 15 km/hr more, it would have taken 30 minutes less for the journey. Find the original speed of the train.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the original speed of the train is x km/hr, we have
90/x – 90/(x + 15) = 1/2
⇒ 1/x – 1/(x + 15) = 1/180
⇒ (x + 15 – x)/x(x + 15) = 1/180
⇒ 15/x(x + 15) = 1/180
⇒ x2 + 15x – 2700 = 0
⇒ x2 + 60x – 45x – 2700 = 0
⇒ x(x + 60) – 45(x + 60) = 0
⇒ (x – 45)(x + 60) = 0
⇒ x = 45 or -60
Thus, the original speed of the train is x = 45 km/hr.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 25
A plane left 30 minutes later than the scheduled time and in order to reach its distance, 1500 km away it has to increase its speed by 250 km/hr from its usual speed. Find its usual speed.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the usual speed of the plain is x km/hr, we have
1500/x – 1500/(x + 250) = 1/2
⇒ 1/x – 1/(x + 250) = 1/3000
⇒ (x + 250 – x)/x(x + 250) = 1/3000
⇒ 250/x(x + 250) = 1/3000
⇒ x2 + 250x – 750000 = 0
⇒ x2 + 1000x – 750x – 750000 = 0
⇒ x(x + 1000) – 750(x + 1000) = 0
⇒ (x – 750)(x + 1000) = 0
⇒ x = 750 or -1000.
Thus, the usual speed of the plain is 750 km/hr.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 26
A boat takes 1 hour longer to go 36 km up a river than to return. If the river flows at 3 km/hr, find the rate at which the boat travels in still water.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the speed of the boat in still water is x km/hr, we have
36/(x – 3) – 36/(x + 3) = 1
⇒ 1/(x – 3) – 1/(x + 3) = 1/36
⇒ (x + 3 – x + 3)/(x + 3)(x – 3) = 1/36
⇒ 6/(x + 3)(x – 3) = 1/36
⇒ 1/(x2 – 9) = 1/216
⇒ x2 = 225
⇒ x = 15 or -15.
Thus, the speed of the boat in still water is x = 15 km/hr.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 27
A man purchased some horses for Rs. 3000. Three of them died, and he sold the rest at Rs. 65 more than what he paid for each horse and thus gained 6% more his outlay. How many horses did he buy?
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the number of horses purchased is x. Then, the price of each horse is Rs. 3000/x.
Now, CP = 3000 and SP = 3000(1 + 6/100) = 3180.
According to question, we have
3180/(x – 3) = 3000/x + 65
⇒ 636/(x – 3) – 600/x = 13
⇒ 636x – 600x + 1800 = 13x(x – 3)
⇒ 36x + 1800 = 13x2 – 39x
⇒ 13x2 – 75x – 1800 = 0
⇒ 13x2 – 195x + 120x – 1800 = 0
⇒ 13x(x – 15) + 120(x – 15) = 0
⇒ (13x + 120)(x – 15) = 0
⇒ x = 15 or -120/13.
Thus, the number of horses purchased is x = 15.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions Class 10 Quadratic Equations Exercise 5E: Ques No 28
A trader bought a number of articles for Rs. 1200. Ten were damaged and he sold each of the rest at Rs. 2 more than what he paid for it, thus getting a profit of Rs. 60 on the whole transaction. Taking the number of article he bought as x, form an equation in x and solve.
S Chand ICSE Maths Solutions:
Let the number of article purchased is x. Then, the price of each article is Rs. 1200/x.
Now, CP = 1200 and SP = 1200 + 60 = 1260.
According to question, we have
1260/(x – 10) = 1200/x + 2
⇒ 625/(x – 10) – 600/x = 1
⇒ 625/(x – 10) – 600/x = 1
⇒ 625x – 600x + 6000 = x(x – 10)
⇒ x2 – 40x – 6000 = 0
⇒ x2 – 100x + 60x – 6000 = 0
⇒ x(x – 100) + 60(x – 100) = 0
⇒ (x + 60)(x – 100) = 0
⇒ x = -60 or 100
Thus, the number of article purchased is x = 100.