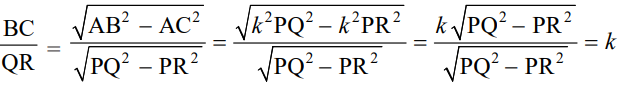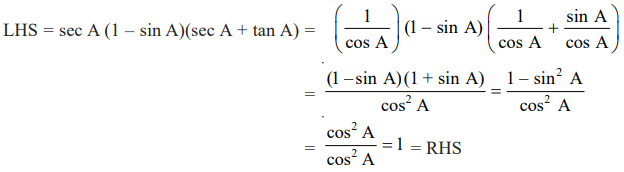Hi students, Welcome to AMBiPi (Amans Maths Blogs). In this article, you will get Introduction to Trigonometry CBSE NCERT Notes Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 PDF. You can download this PDF and save it in your mobile device or laptop etc.
Introduction to Trigonometry CBSE NCERT Notes Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 PDF
Trigonometry
Trigonometry is the study of relationships between the sides and angles of a triangle.
Read More : Real Life Application of Trigonometry
Degree and Radian Conversion
To convert an angle in degree into radian, we need to multiply π/180 to the degree.
To convert an angle in radian into degree, we need to multiply 180/π to the degree.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Examples 1:
Convert 30 degree into radian.
30 degree = 30 x π/180 = π/6 radian.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Examples 2:
Convert 5π/12 radian into degree.
5π/12 radian = 5π/12 x 180/π = 75 degree.
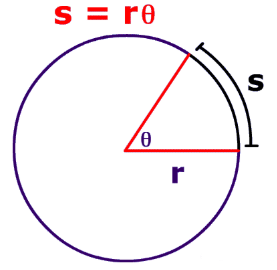
Arc Length of Sector of Circle
If an arc makes an angle θ (in radian) at the center of a circle whose radius is r, then the length of an arc of the arc is s = rθ. Hence, we can say that the angle θ = s/r radian.
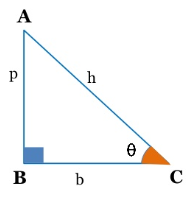
Pythagoras Theorem
In a right angled triangle, the sum of the square of its perpendicular and the square of its base is equal to the square of the hypotenuse. This is known as Pythagorean or Pythagoras theorem.
Thus, in a right triangle, according to the Pythagorean theorem p2 + b2 = h2.
Trigonometric Ratios
In trigonometry, the trigonometric ratios of an acute angle in a right triangle express the relationship between the angle and the length of its sides.
The values of the trigonometric ratios of an angle do not vary with the lengths of the sides of the triangle, if the angle remains the same.
1. Sine of θ is denoted as sinθ and it is the ratio of perpendicular (p) and hypotenuse (h). It means,
sinθ = p/h = AB/AC.
2. Cosine of θ is denoted as cosθ and it is the ratio of base (b) and hypotenuse (h). It means,
cosθ = b/h = BC/AC.
3. Tangent of θ is denoted as tanθ and it is the ratio of perpendicular (p) and base (b). It means,
tanθ = p/b = AB/BC.
4. Cosecant of θ is denoted as cosecθ or cscθ and it is the ratio of hypotenuse (h) and perpendicular (p). It means,
cosecθ or cscθ = h/p = AC/AB.
5. Secant of θ is denoted as secθ and it is the ratio of hypotenuse (h) and base (b). It means,
secθ = h/b = AC/BC.
6. Cotangent of θ is denoted as cotθ and it is the ratio of base (b) and hypotenuse (h). It means,
cotθ = b/p = BC/AB.
Important Result of Trigonometric Ratios
There are following results about the trigonometric ratios.
7. Since sinθ = p/h, cosθ = b/h and tanθ = p/b, then tanθ = (p/h) / (b/h). Thus,
tanθ = sinθ / cosθ.
8. Since sinθ = p/h, cosθ = b/h and cotθ = b/p, then cotθ = (b/h) / (p/h). Thus,
cotθ = cosθ / sinθ.
9. Since sinθ = p/h and cosecθ = h/p, then
sinθ x cosecθ = 1 or sinθ = 1/ cosecθ and cosecθ = 1/ sinθ.
10. Since cosθ = b/h and secθ = h/b, then
cosθ x secθ = 1 or cosθ = 1/ secθ and secθ = 1/ cosθ.
11. Since tanθ = p/b and cotθ = b/p, then
tanθ x cotθ = 1 or tanθ = 1/ cotθ and cotθ = 1/ tanθ.
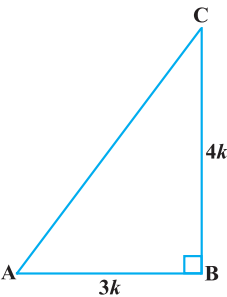
Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Examples 3:
Given that tan A = 4/3 , find the other trigonometric ratios of the angle A.
Since tanA = 4/3 = BC/AB, then let AB = 3k and BC = 4k.
Using Pythagoras theorem, we get AC = 5k.
Thus,
sinA = BC/AC = 4/5,
cosA = AB/AC = 3/5,
cosecA = 1/sinA = 5/4,
secA = 1/cosA = 5/3,
cotA = 1/tanA = 3/4
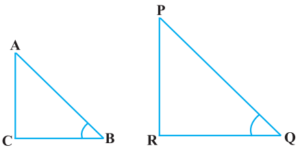
Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Examples 4:
If ∠ B and ∠ Q are acute angles such that sin B = sin Q, then prove that ∠ B = ∠ Q.
Let two right triangles ABC and PQR as below, where sin B = sin Q.
Given that sin B = sin Q ⇒ AC/AB = PR/PQ = k. Then, Now
Now, AC/AB = PR/PQ = BC/QR.
Thus, by SSS Similarity, we get Δ ACB ~ Δ PRQ and therefore, ∠ B = ∠ Q.
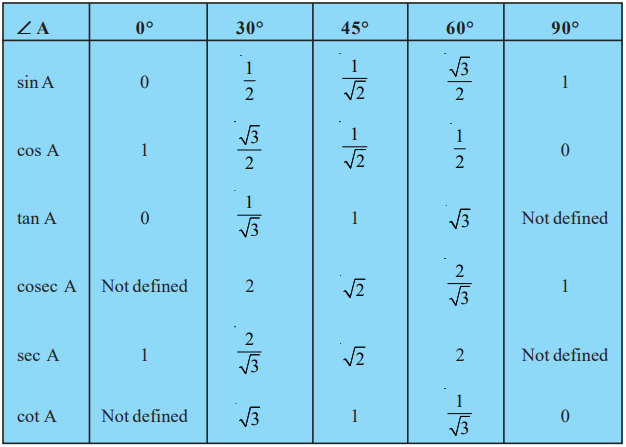
Trigonometric Ratios of Some Specific Angles
Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Examples 5:
If sin (A – B) = 1/2, cos (A + B) = 1/2, 0° < A + B ≤ 90°, A > B, find A and B.
Since sin (A – B) = 1/2 ⇒ A – B = 30° and cos (A + B) = 1/2 ⇒ A + B = 60°
Solving these two equations, we get A = 45° and B = 15°.
Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles
The angles whose sum is 90 degree, then both are called complementary angles.
There are following trigonometric ratios for complementary angles.
sin(90o – θ) = +cosθ
cos(90o – θ) = +sinθ
tan(90o – θ) = +cotθ
cosec(90o – θ) = +secθ
sec(90o – θ) = +cosecθ
cot(90o – θ) = +tanθ
Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Examples 6:
If sin 3A = cos (A – 26°), where 3A is an acute angle, find the value of A.
sin 3A = cos (90° – 3A) ⇒ cos (90° – 3A) = cos (A – 26°) ⇒ 90° – 3A = A – 26° ⇒ A = 29°.
Trigonometric Identities
Using Pythagorean theorem p2 + b2 = h2 and the basic definition of trigonometric ratios, we get three trigonometric identities as below.
sin2θ + cos2θ = 1
sec2θ – tan2θ = 1
cosec2θ – cot2θ = 1
Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Examples 7:
Prove that secA (1 – sin A)(sec A + tan A) = 1.
Click below to get CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter wise Revision Notes PDF.