Welcome to AMBiPi (Read as: एम्बीपाई) (Amans Maths Blogs). JEE Mains and JEE Advanced exams are the engineering entrance exams for taking admission in IITs, NITs and other engineering colleges. In this article, you will get JEE Main Math Previous Year Paper Vectors Questions Answer Keys Solutions.
JEE Mains Mathematics Vectors Questions Bank
JEE Vector Questions No:1
If a × b = b × c = c × a , then a + b + c is equal to
[2002]
Option A: abc
Option B: -1
Option C: 0
Option D: 2
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C : 0
JEE Main Vector Questions No: 2
Let a = 3i – 5j and b = 6i + 3j are two vectors and c is a vector such that c = a × b , then | a | : | b | : | c | is equal to
[2002]
Option A: √34 : √45 : √39
Option B: √34 : √45 : 39
Option C: 34 : 39 : 45
Option D: 34 : 35 : 34
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B : √34 : √45 : 39
JEE Mathematics Vector Questions No: 3
3λc + 2μ(a × b) = 0, then
[2002]
Option A: 3λ + 2μ = 0
Option B: 3λ = 2μ
Option C: λ = μ
Option D: λ + μ = 0
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 3λ = 2μ
JEE Main Math Vector Questions No: 4
If | a | = 5, | b | = 4, | c | = 3 thus what will be the value of | a ∙ b + b ∙ c + c ∙ a |. Given that a + b + c = 0
[2002]
Option A: 25
Option B: 50
Option C: -25
Option D: -30
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: 25
Vector JEE Questions No: 5
If a, b, c are vectors Show that a + b +c = 0 and | a | = 7, | b | = 5, I c | = 3, then the angle between vector b and c is
[2002]
Option A: 600
Option B: 300
Option C: 450
Option D: 900
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: 600
Vector JEE Main Questions No: 6
If a, b, c are vectors such that [a ∙ b ∙ c] = 4, then [ a × b b × c c × a ] is equal to
[2002]
Option A: 16
Option B: 64
Option C: 4
Option D: 8
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 64
Vector for JEE Mains Questions No: 7
If | a | = 4, | b | = 2 and the angle between a and b is (π/6) then (a × b)2 is equal to
[2002]
Option A: 48
Option B:16
Option C: a
Option D: None of These
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 16
Vector Questions for JEE Questions No: 8
If the vectors c, â = xi+ yj + zk and b = j are such that a, c and b form a right handed system then c is
[2002]
Option A: zi – xk
Option B: 0
Option C: yj
Option D: –zi + xk
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: zi – xk
JEE Vector Questions No: 9
Let a, b and c be three unit vectors such that a + b + c = 0, if λ = a ∙ b + b ∙ c + c ∙ a and d = a × b + b x c + c × a, then the ordered pair, (λ,d) is equal to:
[2002]
Option A: (3/2, 3a × c )
Option B: (-3/2, 3c × b)
Option C: (3/2, 3b × c )
Option D: (-3/2, 3a × b )
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: (-3/2, 3a × b )
JEE Mathematics Vector Questions No: 10
If a, b, c are vectors such that a + b + c = 0 and | a | = 7 | b | = 5, | c | = 3 then angle between vector b and c is
[2002]
Option A: 600
Option B: 300
Option C: 450
Option D: 900
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: 600
Vector for JEE Questions No: 11
Let u = i + j, v = i – j and w = i + 2j + 3k . If ñ is unit vector such that u × n = 0 and v × n = 0, then I w ∙ n I is equal to
[2003]
Option A: 0
Option B: 1
Option C: 2
Option D: 3
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: 3
JEE Main Math Vector Questions No: 12
A particle acted on by constant forces 4i + j – 3k and 3i + j – k is displaced from the point i + 2j + 3k to the point 5i + 4j +k . The total work done by the forces is
[2003]
Option A: 20 units
Option B: 30 units
Option C: 40 units
Option D: 50 units
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 40 units
JEE Mains Vector Questions No: 13
The vectors AB = 3i + 4k , and AC = 5i – 2j + 4k are the sides of a triangle ABC. The length of the median through A is
[2003]
Option A: √18
Option B: √72
Option C: √33
Option D: √288
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: √33
JEE Mains Math Vector Questions No: 14
Consider points A, B, C and D with position vectors 7i – 4j + 7k, i – 6j + 10k , –i – 3j + 4k and 5i – j + 5k respectively. Then ABCD is a
[2003]
Option A: Square
Option B: Rhombus
Option C: Rectangle
Option D: None of these
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: None of These
Vector Questions for JEE Questions No: 15
If u, v and w are three non-coplanar vectors, then (u + v – w) ∙ (u – v) × (v – w) equals
[2003]
Option A: 0
Option B: u ∙ v × w
Option C: u ∙ w × v
Option D: 3 u ∙ v × w
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: u × v × w
JEE Vector Questions No:16
a, b, c are 3 vectors, such that a + b + c = 0, | a | = 1, | b |= 2, | c I = 3. then a ∙ b + b ∙ c + c ∙ a is equal to
[2003]
Option A: 0
Option B: -7
Option C: 7
Option D: 1
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: -7
JEE Main Vector Questions No: 17
A tetrahedron has vertices at O (0, 0, 0), A (1, 2, 1), B (2, 1, 3) and C (-1, 1, 2). Then the angle between the faces OAB and ABC will be
[2003]
Option A: cos-1 (19/35)
Option B: cos-1 (17/31)
Option C: 300
Option D: 900
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: cos-1 (19/35)
Vector Questions for JEE Mains Questions No: 18
If
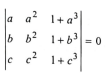
and vectors (1, a, a²), (1, b, b²) and (1, c, c²) are non-coplanar, then the product abc equals
[2003]
Option A: 0
Option B: 2
Option C: -1
Option D: 1
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: -1
JEE Mathematics Vector Questions No: 19
A particle moves towards east from a point A to a point B at the rate of 4 km/h and then towards north from B to C at the rate of 5 km/h. If AB = 12 km and BC = 5 km, then its average speed for its journey from A to C and resultant average velocity direct from A to C are respectively
[2004]
Option A: (17/4) km/h and (13/4) km/h
Option B: (13/4) km/h and (17/4) km/h
Option C: (17/9) km/h and (13/9) km/h
Option D: (13/9) km/h and (17/9) km/h
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: 17/4 km/h and 13/4 km/h
JEE Main Math Vector Questions No: 20
In a right angle ∆ABC, A = ∠90° and sides a, b, c are respectively, 5 cm, 4 cm and 3 cm. If a force F has moments 0, 9 and 16 in N cm. units respectively about vertices A, B and C, then magnitude of F is
[2004]
Option A: 3
Option B: 4
Option C: 5
Option D: 9
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 5
Vector JEE Questions No: 21
Let a, b and c be non-zero vectors such that (a × b) × c = (1/3) | b | | c | | a | . If θ is the acute angle between the vectors b and c, then sin θ equals
[2004]
Option A: 1/3
Option B: √2/3
Option C: 2/3
Option D: 2√2/3
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: 2√2/3
Vector JEE Main Questions No: 22
Let u, v, w be such that | u | = 1, | v | = 2, | w | = 3. If the projection v along u is equal to that of w along u and v, w are perpendicular to each other then | u – v + w | equals
[2004]
Option A: 2
Option B: √7
Option C: √14
Option D: 14
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: √14
Vector Questions for JEE Mains Questions No: 23
If a, b, c are non-coplanar vectors and ???? is a real number, then the vectors a + 2b + 3c, ????b + 4c and (2???? -1) c are non-coplanar for
[2004]
Option A: All values of ????
Option B: All except two values of ????
Option C: All except one value of ????
Option D: No value of ????
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: All except one value of ????
Vector JEE Main Math Questions No: 24
A particle is acted upon by constant forces 4i + j -3k and 3i + j – k which displace it from a point i + 2j + 3k to the point 5i + 4j + k . The work done in standard units by the forces is given by
[2004]
Option A: 40
Option B: 30
Option C: 25
Option D: 15
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: 40
Vector JEE Main Math Questions No: 25
Let a, b and c be three non-zero vectors such that no two of these are collinear. If the vector a 2b is collinear with c and b + 3c is collinear with a (???? being some non-zero scalar) then a + 2b + 6c equals
[2005]
Option A: ????a
Option B: ????b
Option C: ????c
Option D: 0
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: 0
JEE Mains Vector Questions No: 26
Let a = i – k , b= xi + j + (1 – x)k and c = yi + xj + (1 + x – y)k . Then [ a, b, c ]depends on
[2005]
Option A: Only y
Option B: Only x
Option C: Both x and y
Option D: Neither x and y
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: Neither x and y
JEE Mains Math Vector Questions No: 27
If a, b, c are non coplanar vectors and ???? is a real number then [ ???? ( a + b ) ????2 b ???? c ] = [ a b + c b ] for
[2005]
Option A: Exactly one value of ????
Option B: No value of ????
Option C: Exactly three value of ????
Option D: Exactly two value of ????
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: No value of ????
Vector Questions for JEE Questions No: 28
Let a, b and c be distinct non negative numbers. If the vector ai +aj + Ӄ, i + k and ci + cj + bk lie in a plane then c is
[2005]
Option A: The Geometric Mean of a and b
Option B: The Arithmetic Mean of a and b
Option C: Equal to Zero
Option D: The Harmonic Mean of a and b
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: The Geometric Mean of a and b
JEE Vector Questions No:29
For any vector a the value of ( a × i )2 + ( a × j )2 + ( a × k )2 is equal to
[2005]
Option A: 3a2
Option B: a2
Option C: 2a2
Option D: 4a2
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 2a2
JEE Main Vector Questions No: 30
The distance between the line r = 2i – 2j + 3k + ???? ( i – j + 4k ) and the plane r ( i + 5j + k ) = 5 is
[2005]
Option A: ( 10/9 )
Option B: ( 10/3√3 )
Option C: ( 3/10 )
Option D: ( 10/3 )
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B:( 10/3√3 )
| JEE Main Mathematics Previous Year Questions with Solutions: Algebra |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Set, Relations & Functions | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Complex Numbers | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 81 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Sequence & Series | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Quadratic Equations | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Permutations & Combinations | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 94 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Binomial Theorems | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Determinants & Matrices | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Mathematics Previous Year Questions with Solutions: Trigonometry |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Trigonometry Ratios Identities | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Properties of Triangles | 1 to 31 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Trigonometrical Equations | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Inverse Trigonometrical Functions | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Height & Distance | 1 to 27 | |
| JEE Main Mathematics Previous Year Questions with Solutions: Coordinate Geometry |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Cartesian System & Straight Lines | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Circles | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Parabola | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Ellipse | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Hyperbola | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Mathematics Previous Year Questions with Solutions: Differential Equations |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Limit, Continuity & Differentiability | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Differentiations | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Application of Derivative | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Mathematics Previous Year Questions with Solutions: Integral Calculus |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Indefinite Integrals | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Definite Integrals | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Area By Integration | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Mathematics Previous Year Questions with Solutions: Differential Equations |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Differential Equations | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Mathematics Previous Year Questions with Solutions: Vector & 3D Geometry |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Vectors | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 139 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions 3D Geometry | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Mathematics Previous Year Questions with Solutions: Statistics & Probability |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Statistics | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 86 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Probability | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 95 | |
| JEE Main Mathematics Previous Year Questions with Solutions: Miscellaneous |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Mathematical Induction | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |
| JEE Main Previous Year Mathematics Questions Mathematical Reasoning | 1 to 30 | 31 to 60 | 61 to 90 | 91 to 120 | 121 to 150 | |


