Hi CUET aspirants, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMBIPi). In this post, you will get CUET Chemistry Notes Study Materials Surface Chemistry AMBIPi. This CUET Chemistry Notes are designed by analyzing to the CUET Syllabus and CUET Previous Years Questions Papers.
CUET Chemistry Notes
CUET Chemistry Surface Chemistry: Important Points to Remember
There are following important points in this chapter of Surface Chemistry.
CUET Chemistry: Adsorption Sorption Occlusion
The phenomenon of increase in concentration of the molecular species on the surface of the solid than in the bulk is called adsorption.
Both absorption and adsorption often take place side by side. When they occur together, it is called sorption.
A term used for adsorption of gases on a metal surface is known as occlusion.
Adsorption is accompanied by decrease in free energy, i.e, ΔG = -ve when ΔG = TΔS.
Positive adsorption occurs when concentration of adsorbate is more on the surface of absorbent than in the bulk.
Negative adsorption occurs when concentration of adsorbate on the surface is less than that in bulk.
Temperature: Adsorption is an exothermic process, increase in temperature decreases adsorption.
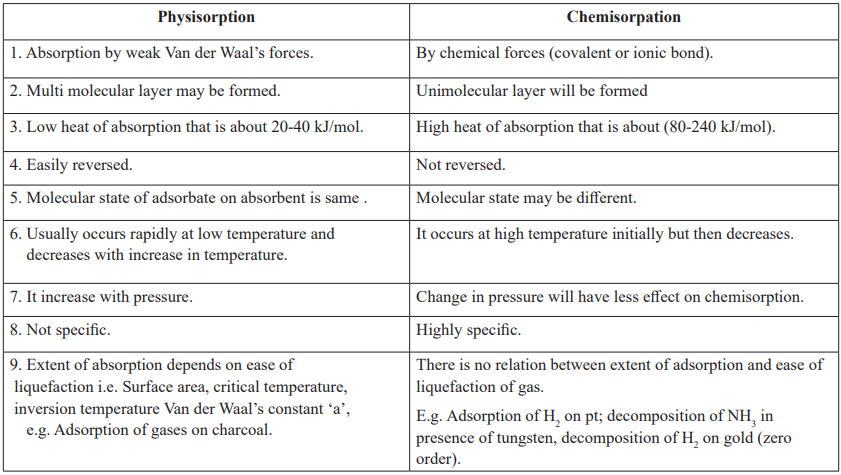
CUET Chemistry: Physisorption vs Chemisorpation
CUET Chemistry: Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm
States that the quantity of gas adsorbed by unit mass of solid adsorbent and pressure at a particular temperature.
Where x is the mass of the gas adsorbed on mass m of the adsorbent at pressure P, temperature. The relationship is generally represented in the form of a curve where mass of the gas adsorbed per gram of the adsorbent is plotted against pressure. These curve indicate that at a fixed pressure, there is decrease in physical adsorption with increase in temperature. These curve always seem to approach saturation at high pressure.
Taking logarithm of equ (1)
When 1/n = 0, x/m = constant, the adsorption is independent of pressure.
When 1/n = 1, x/m = k p, i.e. ∝ p , the adsorption varies directly with pressure.
Limitations of freundlich adsorption isotherm:
It shows deviation at high pressures.
The value of constants k and m is temperature dependent.
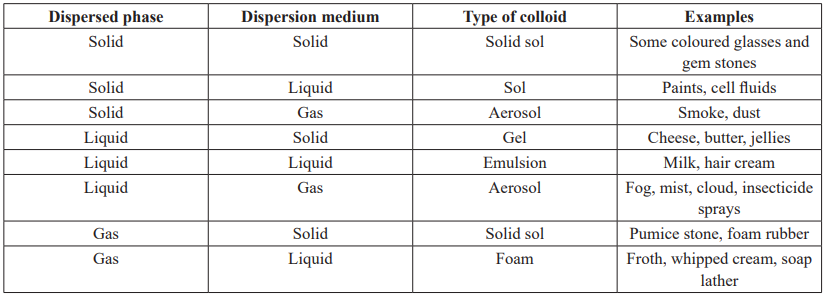
CUET Chemistry: Colloidal State
CUET Chemistry: Classification based on Nature of Interaction Between Dispersed Phase and Dispersion Medium
Lyophilic colloids (Liquid Loving): “The colloidal solutions in which the particles of the dispersed phase have a great affinity for the dispersion medium, are called lyophilic collodis.”
Lyophobic colloids (Liquid Hating): “The colloidal solutions in which there is no affinity between particles of the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium are called lyophobic colloids.”
CUET Chemistry: Optical Properties of Colloidal Solution: Tyndall Effect
When light passes through a sol, its path becomes visible because of scattering of light by particles. It is called Tyndall
effect. This phenomenon was studied for the first time by Tyndall. The illuminated path of the beam is called Tyndall
cone.
CUET Chemistry: Important Points
Coagulation or Flocculation: The process of bringing colloidal particles closer so that they aggregate to form large particles that precipitate and settle down or float on the surface is known as coagulation or flocculation.
Hardy-Schulze rule: Greater the valency of the oppositely charged ion of electrolyte being added, faster the coagulation.
For example:
For – vely charged sol, flocculating power is in the order is Al3+ > Ba2+ > K+
For + vely charged sol, flocculating power is in the order is Fe (CN)64– > PO43– > SO42– > Cl–
Gelling agent is added to stabilize a gel, eg : gelatin
Type of Surfactants:
Soap and detergents are anionic surface.
Cationic surfactants : Quarternary ammonium salts of long chain tertiary amines form detergents which are cationic.
For example: Octadecyl ammonium chloride C18H37N+H3Cl–
Non-inorganic surfactants : These type of surfactants are formed when alcohols reacts with expoxides.
Lesser the criticle micelle concentration (CMC ) of surfactant, more is its surface activity and cleaning action (for detergents).
Protection of colloids and Gold number: Smaller is the gold number, higher is the protective action of the protective agent.
Protective power ∝ 1 / Gold number
Zeta Potential: The potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opposite charge.
CUET Chemistry Mock Test
Now, you have revised the this CUET Chemistry chapter. So, you must need to practice CUET Chemistry Sample Papers. By solving these CUET Chemistry questions, you will be more confident about your CUET preparations.