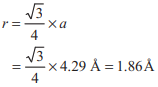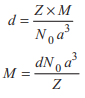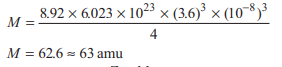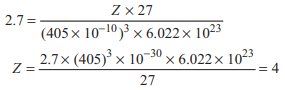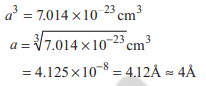Hi CUET aspirants, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMBIPi). In this post, you will get CUET Chemistry Mock Test Solid States AMBIPi. This CUET Chemistry Mock Test is of the Chemistry chapter Solid States. Before solving these CUET Chemistry questions, you must read CUET Chemistry Notes, which helps you to revise CUET Chemistry Syllabus and then you must need to solve CUET Previous Years Questions Papers.
CUET Chemistry Mock Test
CUET Chemistry Question No: 1
All the metallic elements like iron, copper; non-metallic elements like sulphur, iodine and compounds like NaCl, ZnS form
Option A : amorphous solids
Option B : crystalline solids
Option C : polycrystalline solids
Option D : Both (b) and (c)
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: crystalline solids
Most of the solid substances are crystalline in nature. For example, all the metallic elements like iron, copper and silver, non-metallic elements like sulphur, phosphorus and iodine and compounds like sodium chloride, zinc sulphide and naphthalene form crystalline solids.
CUET Exam Chemistry Question No: 2
Some of the physical properties of crystalline solids like refractive index show different values on measuring along different directions in the same crystals. This property is called
Option A : isotropy
Option B : cleavage property
Option C : anisotropy
Option D : None of these
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: anisotropy
CUET UG Chemistry Question No: 3
The lattice points of a crystal of hydrogen iodide are occupied by
Option A : HI molecules
Option B : H atoms and I atoms
Option C : H+ cations and I− anions
Option D : H2 molecules and I2 molecules
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: HI molecules
Since, HI is a covalent molecule, so HI molecules are present at the lattice points of the crystal.
CUET Domain Subject Chemistry Question No: 4
Identify the type of crystal system of the following: (A) KNO3 (B)CaCO3 (C)CaSO4 (D)CuSO4.5H2O
Option A : A-Cubic; B-Triclinic; C-Hexagonal; D-Rhombohedral
Option B : A-Tetragonal; B-Monoclinic; C-Triclinic; D-Hexagonal
Option C : A-Orthorhombic; B-Trigonal; C-Tetragonal; D-Triclinic
Option D : A-Rhombohedral; B-Hexagonal; C-Trigonal; D-Orthorhombic
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: A-Orthorhombic; B-Trigonal; C-Tetragonal; D-Triclinic
(A)KNO3 – Orthorhombic; (B)CaCO3 – Trigonal; (C) CaSO4 – Tetragonal; (D) CuSO4.5H2O – Triclinic
CUET BSc Chemistry Question No: 5
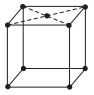
In which of the following structure unit cell shows the triclinic structure?
Option A :
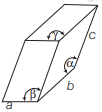
Option B :
Option C :
Option D :
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A:
Fig. (a) represents structure of triclinic crystal system as, a ≠ b ≠ c and α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90°. Whereas, the structures in option (b), (c) and (d) represents end-centred body centred and face-centred cubic.
CUET Entrance Exam Chemistry Question No: 6
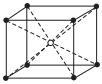
Which primitive unit cell has unequal edge lengths (a ≠ b ≠ c) and all axial angles different from 90°?
Option A : Hexagonal
Option B : Monoclinic
Option C : Tetragonal
Option D : Triclinic
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: Triclinic
Triclinic primitive unit cell has dimensions as, a ≠ b ≠ c and α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90°. Among the seven basic or primitive crystalline systems, the
triclinic system is most unsymmetrical.
In other cases, edge length and axial angles are given as follows:
Hexagonal : a = b ≠ c and α = β = 90°, γ = 120°
Monoclinic : a ≠ b ≠ c and α = γ = 90°, β ≠ 120°
Tetragonal : a ≠ b ≠ c and α = β = γ = 90°
CUET Exam Question No: 7
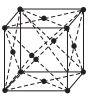
In a face centred cubic lattice, atom A occupies the corner positions and atom B occupies the face centre positions. If one atom of B is missing from one of the face centred points, the formula of the compound is
Option A : A2B
Option B : AB2
Option C : A2B2
Option D : A2B5
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: A2B5
Number of effective A atoms = 8 corners × 1/8 per corner atom share = 1atoms/unit cell
Number of atoms on faces of a cube = 6 atoms
If one B atom is missing from one face, number of B atoms left = 5
∴ Number of effective B atoms = 5 faces × 1/2 per face atom share = 5/2 per unit cell
The formula of the compound is A2B5.
CUET Chemistry Practice Questions No: 8
The number of octahedral void(s) per atom present at a cubic close packed structure is
Option A : 1
Option B : 2
Option C : 3
Option D : 4
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: 1
Number of octahedral voids = Number of atoms in the close packed structure
Since, number of atom = 1; Therefore, number of octahedral void = 1
CUET Chemistry Sample Paper Question No: 9
A compound is formed by cation C and anion A. The anions form hexagonal close packed (hcp) lattice and the cations occupy 75% of octahedral voids. The formula of the compound is
Option A : C3A2
Option B : C3A4
Option C : C4A3
Option D : C2A3
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: crystalline solids
Anions (A) form hexagonal close packed (hcp) lattice, so Number of anions (A) = 6
Number of octahedral voids = Number of atoms in the close packed structure = 6.
Cations (C) occupy 75% of octahedral voids,
so number of cations (C) = 6 × 75/100 = 6 × 3/4 = 9/2
∴ The formula of compound = C9/2A6 = C9A12 = C3A4
CUET Chemistry Mock Test Question No: 10
In a crystalline solid, having formula XY2O4, oxide ions are arranged in cubic close packed lattice, while cations X are present in tetrahedral voids and cations Y are present in octahedral voids. The percentage of tetrahedral voids occupied by X is
Option A : 12.5%
Option B : 25%
Option C : 50%
Option D : 75%
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: crystalline solids
In a cubic close packed lattice of oxide ions, there would be two tetrahedral and one octahedral void per oxide ion.
Since, the formula shows the presence of 4 oxide ions, the number of tetrahedral voids is eight and that of octahedral voids is four. Out of the eight tetrahedral voids, one is occupied by X. ∴ Percentage of tetrahedral voids occupied 1/8 × 100 =12.5 %
CUET Chemistry Question No: 11
Element ‘B ’ forms ccp structure and ‘A ’ occupies half of the octahedral voids, while oxygen atoms occupy all the tetrahedral voids. The structure of bimetallic oxide is
Option A : A2BO4
Option B : AB2O4
Option C : A2B2O
Option D : A4B2O
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: crystalline solids
The number of element ‘B ’ in the crystal structure = 4N
Number of tetrahedral voids = 2N, Number of octahedral voids = N, ∴ Number of ‘A’ in the crystal = N/2 = 2
Number of oxygen (O) atoms = 2N = 2 × 4 = 8, ∴ The structure of bimetallic oxide = A2B4O8 = AB2O4
CUET Exam Chemistry Question No: 12
Sodium metal crystallises in a body centred cubic lattice with a unit cell edge of 4.29 A°. The radius of sodium atom is approximately
Option A : 1.86A°
Option B : 3.22A°
Option C : 5.72A°
Option D : 0.93A°
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: 1.86A
Given, Na metal crystallises in bcc unit cell with unit cell edge, a = 4.29Å.
We have the formula for radius
CUET UG Chemistry Question No: 13
Which of the following is correct order of packing efficiency?
Option A : hcp = fcc > bcc > sc
Option B : sc > bcc > hcp = fcc
Option C : bcc > sc > hcp < fcc
Option D : fcc = hcp > sc > bcc
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: crystalline solids
Packing efficiency for :
Hexagonal close packing (hcp) = 74%
Face-centered cubic close packing (fcc) = 74%
Body centered cubic close packing (bcc) = 68%
and simple cubic (sc) = 52%
Thus, correct order of packing efficiency is :
hcp = fcc > bcc > sc
CUET Domain Subject Chemistry Question No: 14
Which of the following is the ratio of packing density of fcc, bcc and simple cubic structures ?
Option A : 0.92 : 0.70 : 1
Option B : 0.70 : 0.92 : 1
Option C : 1 : 0.92 : 0.70
Option D : 1 : 0.70 : 0.92
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 1 : 0.92 : 0.70
Packing fraction in fcc, bcc and sc are 0.74, 0.68, and 0.52 respectively. Ratio = 0.74/0.74 : 0.68/0.74 : 0.52/0.74 = 1 : 0.92 : 0.90.
CUET BSc Chemistry Question No: 15
A metal has bcc structure and the edge length of its unit cell is 3.04 Å. The volume of the unit cell in cm3 will be
Option A : 1.6 × 10-21 cm3
Option B : 2.81 × 10-23 cm3
Option C : 6.02 × 10-23 cm3
Option D : 6.6 × 10-24 cm3
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 2.81 × 10-23 cm3
Edge length, a = 3.04 Å = 3.04 × 10-8 cm, Thus, Volume of bcc unit cell = a3 = (3.04 × 10-8)3 = 2.81 × 10-23 cm3
CUET Entrance Exam Chemistry Question No: 16
An atom forms face centred cubic crystal with density d = 8.92 g / mL and edge length a = 3.6 × 10−8 cm. The molecular mass of atom in amu is
Option A : 98 amu
Option B : 63 amu
Option C : 32 amu
Option D : 93 amu
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 63 amu
Given, Density (d) = 8.92 g/mL, Edge length (a) = 3.6 × 10−8 cm ⇒ Z = 4 (fcc)
The molecular mass of atom in a lattice can be calculated by using the formula,
CUET Exam Question No: 17
Iron exhibits bcc structure at room temperature. Above 900°C , it transforms to fcc structure. The ratio of density of iron at room temperature to that at 900°C (assuming molar mass and atomic radii of iron remains constant with temperature) is
Option A : 3√3 / 4√2
Option B : 4√3 / 3√2
Option C : √3 / √2
Option D : 1 / 2
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: 3√3 / 4√2
CUET Chemistry Practice Questions No: 18
The cubic unit cell of Al (molar mass 27 g mol−1) has an edge length of 405 pm. Its density is 2.7 g cm–3. The cubic unit cell is
Option A : face centred
Option B : body centred
Option C : primitive
Option D : edge centred
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: face centred
For face centred cubic unit cell, number of atoms are 4
CUET Chemistry Sample Paper Question No: 19
Volume occupied by single CsCl ion pair in a crystalis 7.014 × 10-3 cm. The smallest Cs – Cs internuclear distance is equal to length of the side of the cube corresponding to volume of one CsCl ion pair. The smallest Cs to Cs internuclear distance is nearly
Option A : 4.4 Å
Option B : 4.3 Å
Option C : 4 Å
Option D : 4.5 Å
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 4 Å
As smallest Cs to Cs internuclear distance is equal to length of the side of the cube, i.e. a, therefore,
CUET Chemistry Mock Test Question No: 20
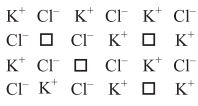
Which kind of defect is shown by the given crystal?
Option A : Schottky defect
Option B : Frenkel defect
Option C : Both Schottky and Frenkel defects
Option D : Substitution disorder
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: crystalline solids
In the given crystal structure, equal number of cations and anions are missing (two K+ and two Cl–) from their normal lattice sites and the crystal maintains its electrical neutrality. Hence, this is Schottky defect.