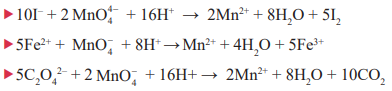Hi CUET aspirants, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMBIPi). In this post, you will get CUET Chemistry Notes Study Materials d-and f-Block Elements AMBIPi. This CUET Chemistry Notes are designed by analyzing to the CUET Syllabus and CUET Previous Years Questions Papers.
CUET Chemistry Notes
CUET Chemistry The d- and f-Block Elements: Important Points to Remember
There are following important points in this chapter of p-Block Elements.
CUET Chemistry: The d-Block Elements
Electronic configuration: (n-1)d1-10 ns1-2
Atomic and Ionic radii: Atomic radii of these elements first decrease and then increases, with the increase in atomic number. Due to lanthanoid contraction, atomic radii increase down the group but radii of third series are virtually the same as those of the corresponding members of second series.
Ionisation energy increases with increase in nuclear charge along each series. The first ionisation enthalpies of Zn, Cd,
Hg are very high because of fully filled configurations.
Physical Properties: With the exceptions of Zn, Cd, Hg and Mn, they have one or more typical metallic structures at normal temperatures.
CUET Chemistry: Order of Properties of The First
Order of Properties of the first series of transition elements
Enthalpy of atomization: V > Ti > Ni > Co > Fe > Cr > Cu > Sc > Mn > Zn
Ionization Enthalpy: Zn > Fe > Co > Cu > Ni > Mn > Ti > Cr > V >Sc
Metallic radii: Sc > Ti > Mn = Zn > V > Cr > Cu > Co = Ni
All Cu11 halides are known except the iodide. In this case, Cu2+ oxidises I– to I2:
2Cu2+ + 4I− → Cu2I2−(s) + I2
Oxidising power: VO2+ < Cr2O72- < MnO4– due to the increasing stability of lower species to which they are reduced.
Mn3+ and Co3+ are the strongest oxidising agents.
Ti2+, V2+, Cr2+ are strong reducing agents and liberate H2 from a dilute acid.
Ti and V are passive to dilute non-oxidising acids at room temperature.
CUET Chemistry: Magnetic Properties
Many of the transition metal ions are paramagnetic
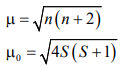
where, S is the total spin (n × s) n is the number of unpaired electrons and s is equal to ½ (representing the spin of an
unpaired electron).
Where n is the number of unpaired electrons and µ is the magnetic moment in units of Bohr magneton (BM).
CUET Chemistry: Chromyl Chloride Test
Chromyl chloride test : A metal chloride on heating with solid K2Cr2O7 and conc.H2SO4 gives red vapours of chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2).
K2Cr2O7 + 4KCl + 6H2SO4 → 2CrO2Cl2 + 6KHSO4+ 3H2O
CUET Chemistry: Oxidising Reactions of KMnO4
In acid solutions:
Sulphurous acid or sulphite is oxidised to a sulphate or sulphuric acid:
5SO32− + 2MnO4− + 6H+→ 2Mn2+ + 3H2O + 5SO42-
In neutral or faintly alkaline solutions:
A notable reaction is the oxidation of iodide to iodate:
Thiosulphate is oxidised almost quantitatively to sulphate
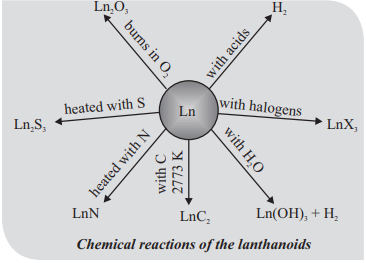
CUET Chemistry: The f-Block Elements
It is also called inner – transition elements
Electronic configuration: (n-2)f1-14, (n-1)d0-10, ns2
Oxidation states: In the lanthanoids, La(III) and Ln(III) compounds are predominant.
The hardness increases with increasing atomic number, samarium being steel hard.
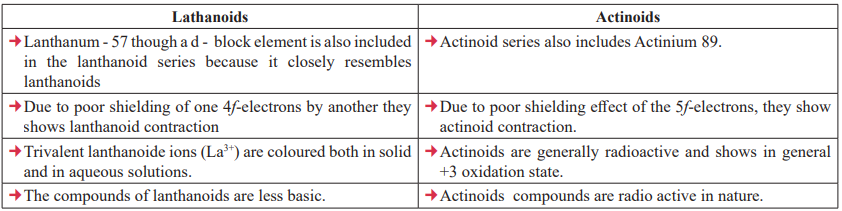
The Actinoids:
The general trend in lanthanoids is observable in the actinoids as well. There is a gradual decrease in the size of atoms or M3+ ions across the series. This may be referred to as the actinoid contraction (like lanthanoid contraction).
The contraction is, however, greater from element to element in this series resulting from poor shielding by 5f electrons.
Hydrochloric acid attacks all metals but most are slightly affected by nitric acid owing to the formation of protective oxide layers; alkalies have no action.
CUET Chemistry: Lanthanoids & Actinoids
The radii of members of 5d-series are similar to those of corresponding members of 4d-series due to lanthanoid contraction. eg: Zr and Hf have almost same radii and due to same radii they have similar physical and chemical properties. That’s why they are also known as chemical twins of the periodic table.
CUET Chemistry: Some Applications of d- and f-Block Elements
TiO – the pigment industry
MnO2– use in dry battery cells.
V2O5 catalyses the oxidation of SO2 in the manufacture of sulphuric acid.
TiCl4 with Al(CH3)3 forms the basis of the Ziegler catalysts used to manufacture polyethylene (polythene).
Iron catalysts are used in the Haber process for the production of ammonia from N2/H2 mixtures.
Nickel catalysts enable the hydrogenation of fats to proceed
In the Wacker process the oxidation of ethyne to ethanal is catalysed by PdCl2.
Nickel complexes are useful in the polymerisation of alkynes and other organic compounds such as benzene.
The photographic industry relies on the special lightsensitive properties of AgBr.
CUET Chemistry Mock Test
Now, you have revised the this CUET Chemistry chapter. So, you must need to practice CUET Chemistry Sample Papers. By solving these CUET Chemistry questions, you will be more confident about your CUET preparations.