Hi CUET aspirants, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMBIPi). In this post, you will get CUET Chemistry Notes Study Materials Coordination Compounds AMBIPi. This CUET Chemistry Notes are designed by analyzing to the CUET Syllabus and CUET Previous Years Questions Papers.
CUET Chemistry Notes
CUET Chemistry Coordination Compounds: Important Points to Remember
There are following important points in this chapter of Coordination Compounds.
CUET Chemistry: Introduction to Coordination Compounds
Complex compounds in which the metal atoms are bound to a number of anions or neutral molecules, such compounds are called coordination compounds.
Chlorophyll, haemoglobin and vitamin B12 are coordination compounds of magnesium, iron and cobalt respectively.
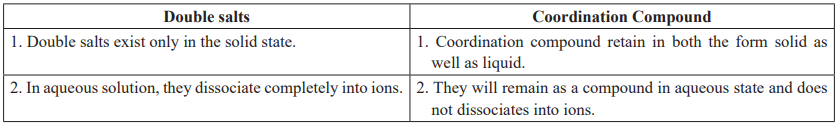
Effective Atomic Number (EAN): Predicting stability of a coordination compound.
EAN = Atomic weight – Electron lost + Electron gained.
CUET Chemistry: Coordination Number, Homoleptic & Heteroleptic Complex
Coordination number: The coordination number (CN) of a metal ion in a complex can be defined as the number of ligand donor atoms to which the metal is directly bonded.
Homoleptic and heteroleptic complexes: Complexes in which a metal is bound to only one kind of donor groups, e.g., [Co(NH3)6]3+, are known as homoleptic.
Complexes in which a metal is bound to more than one kind of donor groups, e.g., [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+, are known as heteroleptic.
CUET Chemistry: Rules for Naming Coordination Compounds
The anion is named after the cation.
The complex part is written as one word and name of coordination compounds is started with a small letter.
In naming coordination sphere, ligand are named first in alphabetical order followed by metal atom and then oxidation state of metal by roman numeral in parenthesis.
Name of anionic ligand ends in – O.
Name of cationic ligand ends in – ium.
The prefixes di- , tri- tetra- , penta- and hexa- are used to indicate the number of each ligand. If the ligand name includes such a prefix, the ligand name should placed in parentheses and preceded by bis-(2), tris (3), tetrakis (4), penta kis(5), hexakis(6).
[Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3]Cl3 is named as: triamminetriaquachromium(III) chloride.
[Co(H2NCH2CH2NH2)3]2(SO4)3 is named as: tris(ethane-1, 2-diammine)cobalt(III) sulphate.
[Ag(NH3)2][Ag(CN)2] is named as: diamminesilver(I) dicyanoargentate(I)
CUET Chemistry: Valence Bond Theory
This theory was put forward by L. Pauling.
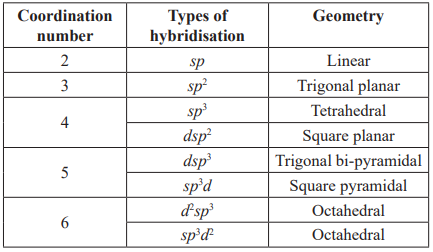
Metal atom/ion must have vacant d-orbitals of equal energy equal to the number of ligands to be attached. These orbitals are obtained by hybridisation.
The shapes of complex are depending upon the type of hybridisation.
Limitation of VBT:
Fails to explain the strength of magnetic field, relative energies of different shapes, colour and spectral properties of complex.
CUET Chemistry: Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
In crystal field theory, the interaction between ligands and metal ion is purely electrostatic.
In the influence of ligand field, degeneracy of the d-orbital is destroyed and it splits into two or more energy levels and split the d-orbital into two group tg and t2g, and the energy difference between these two is known as field splitting parameters. (Δo).
The increasing order of Δo is:
I– < Br– < SCN– < Cl– < S2- < F– < OH– < C2O42- < H2O < NCS– < EDTA4- < NH3 < en < CN– < CO
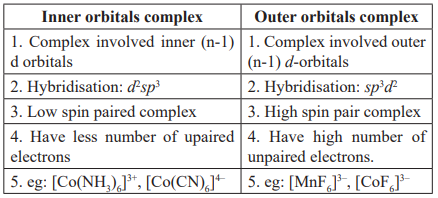
If Δo > p (Pairing energy) (i.e, Δo large, strong field ligand) → electron pair-up in t2g orbital → forms low spin complex.
If Δo < p (Δo small, weak field ligand) → electron spread out → form high spin complex.
Stability:
More is the stability greater the charge on central metal ion.
More is the stability more the basic strength of ligand.
Increases the stability of complex on formation of chelate ring.
More is the stability, smaller the size of metal ion.
More is the electronegative and polarising power of the metal ion, more stable is the complex.
Limitation of CFT:
CFT treat the metal ligand bond as purely ionic and do not consider the covalent character of bonding between ligand
and central atom.
CUET Chemistry: Bonding in Metal Carbonyls
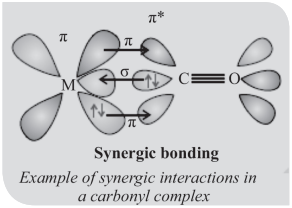
The M–C σ bond is formed by the donation of lone pair of electrons on the carbonyl carbon into a vacant orbital of the metal.
The M–C π bond is formed by the donation of a pair of electrons from a filled d-orbital of metal into the vacant anti-bonding π* orbital of carbon monoxide.
The metal to ligand bonding creates a synergic effect which strengthens the bond between CO and the metal.
CUET Chemistry: Application & Importance of Coordination Compounds
Coordination compounds find use in many qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. E.g., EDTA, DMG dimethylglyoxime), α–nitroso–β– naphthol, cupron
Coordination compounds are used as catalysts for many industrial processes.
Eg: rhodium complex, [(Ph3P)3RhCl], a Wilkinson catalyst, is used for the hydrogenation of alkenes.
EDTA is used in the treatment of lead poisoning.
Some coordination compounds of platinum effectively inhibit the growth of tumors.
Examples are Ferrocene & Cisplatin
CUET Chemistry Mock Test
Now, you have revised the this CUET Chemistry chapter. So, you must need to practice CUET Chemistry Sample Papers. By solving these CUET Chemistry questions, you will be more confident about your CUET preparations.