Hi CUET aspirants, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMBIPi). In this post, you will get CUET Chemistry Mock Test Surface Chemistry AMBIPi. This CUET Chemistry Mock Test is of the Chemistry chapter Surface Chemistry . Before solving these CUET Chemistry questions, you must read CUET Chemistry Notes, which helps you to revise CUET Chemistry Syllabus and then you must need to solve CUET Previous Years Questions Papers.
CUET Chemistry Mock Test
CUET Chemistry Question No: 1
In case of adsorption,
Option A : a particle present in the bulk experience an unbalanced force
Option B : unbalanced forces are responsible for the interaction between adsorbate and adsorbent
Option C : extent of adsorption increases with increase of surface area per unit mass of adsorbent at a given temperature and pressure
Option D : All of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: All of the above
CUET Exam Chemistry Question No: 2
Which of the following activity does not take place at the time of adsorption?
Option A : Residual attractive forces decreases
Option B : Surface energy decreases
Option C : Heat releases
Option D : Heat is absorbed
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: Heat is absorbed
During adsorption, there is always a decrease in the residual forces of the surface, i.e. there is decrease in surface energy which appears as heat and, thus heat is released. Therefore, adsorption is an exothermic process.
ΔH = -ve (always)
CUET UG Chemistry Question No: 3
In Freundlich adsorption isotherm, the value of 1/ n is
Option A : between 0 and 1 in all cases
Option B : between 2 and 4 in all cases
Option C : 1 in case of physical adsorption
Option D : 1 in case of chemisorption
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: between 0 and 1 in all cases
In Freundlich adsorption isotherm, x/m = kp1/n
where, x = amount of adsorbate
m = amount of adsorbent
The value of n is always greater than 1.
So, the value of 1/n lies between 0 and 1 in all cases.
CUET Domain Subject Chemistry Question No: 4
When pressure is low, the fraction of the surface covered during adsorption follows:
Option A : Zero order kinetics
Option B : First order kinetics
Option C : Second order kinetics
Option D : Fractional order kinetics
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: First order kinetics
At low pressure, curve is almost straight line, i.e.
x/m α p or x/m = kp
Hence, it follows first order kinetics.
CUET BSc Chemistry Question No: 5
Which of the following is/are generally used for the removal of the coloured impurities from the solutions?
Option A : Charcoal
Option B : Silica gel
Option C : Both (a) and (b)
Option D : Anhyd. CaCl2
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: Charcoal
Animal charcoal removes coloured impurities of solutions by adsorbing.
CUET Entrance Exam Chemistry Question No: 6
Which of the following substance acts as a catalyst for the following reaction?
2 KCIO3 → 2 KCI + 3 02
Option A : MnO2
Option B : O2
Option C : HCl
Option D : All of these
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: MnO2
In the given reaction, 2 KCI03 → 2 KCI + 3O2;
When little amount of MnO2 is added, the decomposition takes place at lower temperature and rate of reaction also increases. Moreover, amount of MnO2 remains unchanged during the reaction.
CUET Exam Question No: 7
Which of the following are the examples of heterogeneous catalysis?
Option A : Haber’s process
Option B : Ostwald’s process
Option C : Oxidation of SO2 into SO3 in presence of Pt
Option D : All of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: All of the above
Number of effective A atoms = 8 corners × 1/8 per corner atom share = 1atoms/unit cell
Number of atoms on faces of a cube = 6 atoms
If one B atom is missing from one face, number of B atoms left = 5
∴ Number of effective B atoms = 5 faces × 1/2 per face atom share = 5/2 per unit cell
The formula of the compound is A2B5.
CUET Chemistry Practice Questions No: 8
The activity of a catalyst depends upon the strength of
Option A : chemisorption
Option B : physisorption
Option C : solution
Option D : None of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: chemisorption
CUET Chemistry Sample Paper Question No: 9
The enzyme invertase converts the cane sugar into
Option A : glucose
Option B : fructose
Option C : glucose + fructose
Option D : None of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: glucose + fructose
The enzyme invertase converts the cane sugar into
glucose and fructose. i.e.
Cane Sugar → glucose + fructose
CUET Chemistry Mock Test Question No: 10
Activators promoting catalytic actions are generally
Option A : metal ions
Option B : non-metal ions
Option C : metalloids ions
Option D : All of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: metal ions
Activators promoting catalytic actions are generally metal ions (Na+ , Mn2+, CO2+, CU2+). ). These get weakly bonded to enzyme molecules and therefore promote catalytic action.
CUET Chemistry Question No: 11
Lyophobic colloids are not stable because
Option A : they coagulate by heating them or with the addition of electrolytes
Option B : they coagulate by freezing them or with the addition of electrolytes
Option C : they do not coagulate by freezing them with the electrolytes
Option D : they do not coagulate by heating them with the electrolytes
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: they coagulate by heating them or with the addition of
electrolytes
Lyophobic colloids are readily precipitated (or coagulated) on addition of small amounts of electrolytes or by heating, hence they are not stable.
CUET Exam Chemistry Question No: 12
Gold sols and sulphur sols are the examples of
Option A : multimolecular colloids
Option B : macromolecular colloids
Option C : associated colloids
Option D : All of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: multimolecular colloids
Sulphur sol (consists of particles containing a thousands or more of S8 sulphur molecules and gold sol (containing particles of various sizes having many atoms) are the examples of multimolecular colloids.
CUET UG Chemistry Question No: 13
In the cleansing action of soaps represented by the given figures,
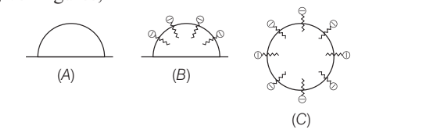
Figure ‘C’ show the structure of
Option A : aggregated colloids
Option B : macromolecular colloids
Option C : Both (a) and (b)
Option D : multimolecular colloids
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: aggregated colloids
In the given figures, Fig. C shows the structure of aggregated colloids or micelles.
CUET Domain Subject Chemistry Question No: 14
Which of the following processes is involved in Bredig’s arc method?
Option A : Only dispersion
Option B : Only condensation
Option C : Dispersion as well as condensation
Option D : Diffusion
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: Dispersion as well as condensation
Bredig’s arc method involves the process of both dispersion as well as condensation. Colloidal sols of metals such as gold, silver, platinum etc., can be prepared by this method.
CUET BSc Chemistry Question No: 15
Purification of the colloidal solution is carried out by
Option A : dialysis
Option B : electrodialysis
Option C : ultrafiltration
Option D : All of these
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: All of these
CUET Entrance Exam Chemistry Question No: 16
Tyndall effect is observed only, when
Option A : the diameter of the dispersed particles is not much smaller than the wavelength of light used.
Option B : there is high difference between the refractive indices( μ) of the dispersion medium and dispersed phase.
Option C : refractive indices ( μ ) of both dispersed medium and dispersed phase are equal to each other.
Option D : Both (a) and (b)
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: Both (a) and (b)
Tyndall effect is the scatttering of light by sol particles, which cannot be affected by charge on them. Other given options such as coagulation, electrophoresis and electroomosis depend on charge particles. Thus, option (d) is correct.
CUET Exam Question No: 17
Which property of colloidal solutions is independent of charge on the colloidal particles?
Option A : Coagulation
Option B : Electrophoresis
Option C : Electroosmosis
Option D : Tyndall effect
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: Tyndall effect
CUET Chemistry Practice Questions No: 18
Which of the following is an example of the negatively charged sols?
Option A : FeCI3 + NaOH
Option B : FeCI3 + hot water
Option C : When Ag+ is absorbed by AgI in solution of AgNO3 and KI
Option D : All of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: FeCI3 + NaOH
Mixure of FeCI3 and NaOH form the negatively charged sol, while other given forms are positively charged sols
CUET Chemistry Sample Paper Question No: 19
Which of the following is the most acceptable reason to explain the charge on sol particles?
Option A : Electron capture by sol particles during electro dispersion
Option B : Preferential adsorption of ions from solution
Option C : Formulation of electrical double layer
Option D : None of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: Preferential adsorption of ions from solution
The sol particles acquire positive or negative charge by preferential adsorption of the positive or negative from solution.
CUET Chemistry Mock Test Question No: 20
The potential difference between the fixed layer and diffused layer of opposite charges in the colloidal system is known as
Option A : Zeta potential
Option B : gravitational potential
Option C : standard potential
Option D : ionic potential
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: Zeta potential
The potential difference between fixed layer and diffused layer of opposite charges of a colloidal sol is termed as electro kinetic or Zeta potential.
