Hi CUET aspirants, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMBIPi). In this post, you will get CUET Chemistry Mock Test Electrochemistry AMBIPi. This CUET Chemistry Mock Test is of the Chemistry chapter Electrochemistry. Before solving these CUET Chemistry questions, you must read CUET Chemistry Notes, which helps you to revise CUET Chemistry Syllabus and then you must need to solve CUET Previous Years Questions Papers.
CUET Chemistry Mock Test
CUET Chemistry Question No: 1
Electrolytic cell is a device
Option A : in which a non-spontaneous chemical reaction is carried out at the expense of electrical energy
Option B : in which a spontaneous chemical reaction is carried out to generate electrical energy
Option C : in which applied opposite potential is less than the cell potential
Option D : Both (a) and (c)
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: in which a non-spontaneous chemical reaction is carried out at the expense of electrical energy
When Eext > generated, the cell behaves like an electrolytic cell. In this cell, a non-spontaneous reaction is carried out at the expense of electrical energy.
CUET Exam Chemistry Question No: 2
KCl solution is generally used to determine the cell constant because
Option A : it is highly ionic in nature
Option B : its conductivity is known accurately at various concentration and different temperatures
Option C : size of cations and anions are comparable
Option D : All of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: its conductivity is known accurately at various concentration and different temperatures
Conductivity of KCl solution is known accurately at various concentrations and different temperatures, so it is generally used in conductivity cell to measure cell constant.
CUET UG Chemistry Question No: 3
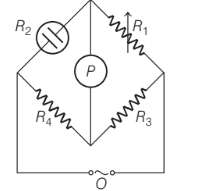
Which of the following information is false for the below given figure?
Option A : This assembly is used for measuring conductivity of solution
Option B : O is an oscillator, i.e. a source of AC power
Option C : P is the conductivity cell
Option D : Unknown resistance is measured by using the formula, R2 = R1 R4 / R3
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: P is the conductivity cell
Wheatstone bridge consists of two resistance, R3 and R4 and a variable resistance R1 and conductivity cell having unknown resistance R2. O is the source of AC power called oscillator. Under no current condition, minimum or no sound can be heard from the earphone, P (a detector). The unknown resistance, R2 is calculated as R2 = R1 R4/ R3
CUET Domain Subject Chemistry Question No: 4
The conductance of electrolytic solution kept between the electrodes of conductivity cell at unit distance but having area of cross-section large enough to accommodate sufficient volume of solution is called
Option A : limiting molar conductivity
Option B : molar conductivity
Option C : conductivity
Option D : All of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: molar conductivity
Molar conductivity (Λ m) is defined as the conductance of the electrolytic solution kept between the electrodes of a conductivity cell at unit distance but having area of cross-section large enough to accommodate sufficient volume of solution that contains one mole of the electrolyte.
CUET BSc Chemistry Question No: 5
The resistance of the cell containing KCl solution at 23°C was found to be 55 Ω. Its cell constant is 0.616 cm−1. The conductivity of KCl solution (Ω−1 cm−1) is
Option A : 1.21 x10-3
Option B : 1.12 x 10-2
Option C : 1.12x 10-3
Option D : 1.21 x 10-2
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 1.12 x 10-2
Conductivity, (κ) = Cell constant/ Resistance = 0.616 cm-1/ 55Ω = 1.12 x 10-2 Ω-1 cm-1
CUET Entrance Exam Chemistry Question No: 6
If resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 2 mol L−1 KCl solution is 100 Ω.The resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.2 mol L −1 KCl solution is 520 Ω. Then the conductivity of 0.2 mol L −1 KCl solution will be (Given the conductivity of 1 mol L-1 KCI solution is 1.29 S/m)
Option A : 0.248 S cm−1
Option B : 0.248 S m−1
Option C : 2.48 S cm−1
Option D : 2.48 S m−1
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 0.248 S m−1B
The cell constant is given by the equation: Cell constant, G * = conductivity × resistance = 1.29 S/ m x100 Ω = 129m
Conductivity of 0.2 mol L-1 KCl solution = cell constant/ resistance = G*/R = 129m-1 / 520 Ω = 0.248 S m-1
CUET Exam Question No: 7
“Limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as sum of the individual contributions of anion and cation of the electrolyte”. Which law states the above statement?
Option A : Henry’s law
Option B : Debye Onsager’s law
Option C : Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions
Option D : All of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions
According to Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration, “the limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte”.
CUET Chemistry Practice Questions No: 8
If boiling point of water is 100°C. How much gram of NaCI is added in 500g of water to increase its boiling point by approax 1°C? [( Kb) H2O= 0.52 kg mol −1]
Option A : 2.812 g
Option B : 28.12 g
Option C : 14.06 g
Option D : 7.03 g
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: 2.812 g
Galvanic cell that are used to convert the energy of combustion of fuels like hydrogen, methane, methanol, etc., directly into electrical energy is called fuel cells.
CUET Chemistry Sample Paper Question No: 9
Calculate the standard cell potential for the following
Galvanic cell,
Cr| Cr3+ || Cd2+ | Cd
[Given, E Cr3+/ Cr = 0.74 V and E cd2+/ Cd = -0.40 V]
Option A : 0.74 V
Option B : – 0.34 V
Option C : + 0.34 V
Option D : 1.14 V
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: + 0.34 V
Standard cell potential for the given cell, Ecell = E cd2+/ cd – ECr3+/ Cr = 0.40 – (0.740)
= +0.34 V
CUET Chemistry Mock Test Question No: 10
Standard electrode potential for Sn4+ / Sn2+ couple is + 0.15 V and that for the Cr3+/ Cr couple is – 0.74 V. These two couples in their standard state are connected to make a cell. The cell potential will be
Option A : +1.83 V
Option B : +1.19 V
Option C : + 0.89 V
Option D : +0.18 V
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: + 0.89 V
The cell potential is given as, Ecell = Ecathode (RP) -Eanode (RP)
Ecell = 0.15 – (-0.74) = +0.89 V
CUET Chemistry Question No: 11
Vapour pressure of pure benzene is 119 torr and that of toluene is 37.0 torr at the same temperature. Mole fraction of toluene in vapour phase which is in equilibrium with solution of benzene and toluene having a mole fraction of toluene 0.50, will be
Option A : 0.137
Option B : 0.237
Option C : 0.435
Option D : 0.205
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 0.237
During charging: Pb + SO 2-4 → Pb SO4 + 2e–
⇒ 1 F = 1g – equiv. of PbSO4 ⇒ 303/2 g Pb SO4
0.05 F = 303/2 X 0.05 g pf Pb SO4 = 7.75 g of PbSO4
CUET Exam Chemistry Question No: 12
At room temperature, a dilute solution of urea is prepared by dissolving 0.60 g of urea in 360 g ofwater. If the vapour pressure of pure water at this temperature is 35 mm Hg, lowering of vapour pressure will be (Molar mass of urea = 60 g mol −1)Sodium metal crystallises in a body centred cubic lattice with a unit cell edge of 4.29 A°. The radius of sodium atom is approximately
Option A : 0.027 mm Hg
Option B : 0.031 mm Hg
Option C : 0.017 mm Hg
Option D : 0.028 mm Hg
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: 0.028 mm Hg
Na+ + e– → Na (Hg) 2 CI- → CI 2 + 2e- Moles of NaCl electrolysed = 4 x 500/1000 = 2.0 Two Faraday of electric charge is required for electrolysis of
2 moles of NaCl. Total coulombs = × 2 96500 = 193000 C.
CUET UG Chemistry Question No: 13
Relative lowering of vapour pressure is a colligative property because
Option A : it depends on the concentration of a non-electrolyte solute in solution and does not depend on the nature of
the solute molecules
Option B : it depends on number of particles of electrolytic solute in solution as well as on the nature of the solute particles
Option C : it depends on the concentration of a non-electrolyte solute in solution as well as on the nature of the solute
molecules
Option D : it depends on the concentration of an electrolyte or non-electrolyte solute in solution as well as on the nature of solute molecules
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: it depends on number of particles of electrolytic solute in solution as well as on the nature of the solute particles
CUET Domain Subject Chemistry Question No: 14
A hydrogen gas electrode is made by dipping platinum wire in a solution of HCl at pH =10 and by passing hydrogen gas around the platinum wire at 1 atm pressure. The oxidation potential of electrode would be
Option A : 0.059 V
Option B : 0.59 V
Option C : 0.118 V
Option D : 0.18 V
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 0.59 V
CUET BSc Chemistry Question No: 15
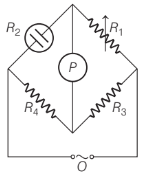
Which of the following information is false for the below given figure?
Option A : This assembly is used for measuring conductivity of solution
Option B : O is an oscillator, i.e. a source of AC power
Option C : P is the conductivity cell
Option D : Unknown resistance is measured by using the formula, R2 = R1 R4/ R3
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: P is the conductivity cell
Wheatstone bridge consists of two resistance, R3 and R4 and a variable resistance R1 and conductivity cell having unknown resistance R2 . O is the source of AC power called oscillator. Under no current condition, minimum or no sound can be heard from the earphone, P (a detector). The unknown resistance, R2 is calculated as R2 = R1 R4/ R3
CUET Entrance Exam Chemistry Question No: 16
In the given reaction. The equilibrium constant for this reaction will be
2 Cu+ (aq) ⇔ Cu2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
E Cu+/cu = 0.6 V E Cu2+/cu = 0.41 v
Option A : 2 76 102
Option B : 2 76 104
Option C : 2 76 106
Option D : 2 76 108
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 2 76 106
CUET Exam Question No: 17
The anodic half-cell of lead-acid battery is recharged using electricity of 0.05 Faraday. The amount of PbSO4 electrolysed in g during the process is(Molar mass of PbSO4 303g mol-1
Option A : 11.4
Option B : 7.6
Option C : 15.2
Option D : 22.8
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 7.6
CUET Chemistry Practice Questions No: 18
In the given mercury cell, The reaction occuring at cathode will be
Option A : Zn(Hg) 2OH– → ZnO(s) H2O 2 + 2e–
Option B : HgO H2O + 2e– → Hg (l) + 2 OH–
Option C : Zn + 2 OH– → ZnO (s) + H2O + 2e–
Option D : Zn(Hg) + HgO(s) → ZnO (s) + Hg (l)
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: HgO H2O + 2e– → Hg (l) + 2 OH–
The reaction takes place in the given cell are as follows:
Anode Zn(Hg) + 2OH– ZnO (aq) → ZnO (s) + H2O + 2e–
Cathode HgO (s) + H2O + 2e–→ Hg (l)
The overall reaction is Zn(Hg) + HgO (s) → ZnO (s) + Hg (l)
CUET Chemistry Sample Paper Question No: 19
When aqueous sodium chloride solution is electrolysed
Option A : at cathode H+ is reduced into H2 instead of Na +
Option B : at cathode Na + is reduced to Na
Option C : Cl− is oxidised into Cl2 at cathode
Option D : Both (b) and (c)
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: at cathode H+ is reduced into H2 instead of Na +
When aqueous solution of NaCl is electrolysed, there is a
competition between the following reduction reactions at cathode.
Na+ + e- → Na ; E cell = – 271 V H+ + e– → 1/2 H2 ; Ecell = 0.00 V
The reaction with higher value of E° is preferred and therefore, the second reaction occurs at cathode, i.e. H+ is reduced instead of Na+
CUET Chemistry Mock Test Question No: 20
Zn(s) + Cu 2+ (aq)→ Zn2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
The above redox reaction is used in
Option A : Galvanic cell
Option B : Daniell cell
Option C : Voltaic cell
Option D : All of these
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: All of these