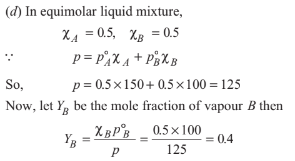Hi CUET aspirants, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMBIPi). In this post, you will get CUET Chemistry Mock Test Solutions AMBIPi. This CUET Chemistry Mock Test is of the Chemistry chapter Solutions. Before solving these CUET Chemistry questions, you must read CUET Chemistry Notes, which helps you to revise CUET Chemistry Syllabus and then you must need to solve CUET Previous Years Questions Papers.
CUET Chemistry Mock Test
CUET Chemistry Question No: 1
If two bottles A and B contain 1 M and 1 m aqueous solution of sulphuric acid respectively,
Option A : A is more concentrated than B
Option B : B is more concentrated than A
Option C : Concentration of A is equal to concentration of B
Option D : It is not possible to compare the concentration
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: B is more concentrated than A
1 MH2 SO4 means 1 mole of H2SO4 dissolved in 1000 cc of solution, whereas 1 m H2SO4 means 1 mole of H2SO4 dissolved in 1000 g of water. Total volume of 1 m solution will be greater than 1000 cc due to extra mole of H2O 2 4. Hence, number of moles per1000 cc will be less than 1 mole. Thus, bottle B containing 1 m aqueous solution is more concentrated than bottle A containing 1 M aqueous solution.
CUET Exam Chemistry Question No: 2
What is the percentage of solute in the resultant solution, if it is obtained by mixing 300g of 30% and 200g of 20% solution by weight?
Option A : 50%
Option B : 26%
Option C : 62%
Option D : 32%
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 26%
Solute in 300 g of 30% solution = 90 g Solute in 200 g of 20% solution = 40 g Total grams of solute = 130 g
Total grams of solution = 300 + 200 = 500 g, % of solute in the final solution = 130 /500 x 100 = 26%
CUET UG Chemistry Question No: 3
What is the molarity of K+ in aqueous solutions that contains 17.4 ppm of K2SO4 (Molar Mass = 14.4 g mol-1 ) ?
Option A : 2 x10−2 M
Option B : 2 x10−3 M
Option C : 4 x10−4 M
Option D : 2 x10−4 M
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: 2 x10−4 M
K2SO4 is 17.4 ppm, i.e. 106 mL has 17.4 g K2SO4
1 L (103 mL) has K2SO4 = 17.4 x 103/ 106 = 0.0174 /174 mol/L [K2SO4 ⇔ 2K+ + SO2-4 [K+] = 2x 10-4M
CUET Domain Subject Chemistry Question No: 4
A 5.2 molal aqueous solution of methyl alcohol, CH3 OH 3 is supplied. What is the mole fraction of methyl alcohol in the solution?
Option A : 1.100
Option B : 0.090
Option C : 0.086
Option D : 0.050
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 0.086
CUET BSc Chemistry Question No: 5
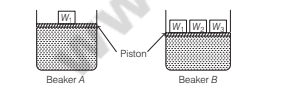
For a solution of gases in a solvent, consider a system as shown below : Which of the following beaker will have the greater solubility of a gas?
Option A : Beaker B
Option B : Beaker A
Option C : Both will have same solubility
Option D : Solubility remains unaffected by change in weights.
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: Beaker B
Beaker B will have greater solubility of a gas in liquid than Beaker A. This is because, solubility of a gas in liquid directly proportional to the pressure of a gas. On increasing the weight over the piston, the pressure over the solution phase increases.
CUET Entrance Exam Chemistry Question No: 6
Calculate the concentration of nitrogen present in the water. Assuming that, the temperature is 25°C, total pressure is 1 atm and mole fraction of nitrogen is 0.78 [KH for nitrogen 8.42 x 10-7 M/mm Hg]
Option A : 4.99 M
Option B : 4.99 10-2 M
Option C : 4.99 10-4 M
Option D : None of these
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 4.99 10-4 M
pN2 = χN2 x Ptotal i.e 1 atm = 7.60 mm Hg
pN2 = 0.78 x 1 atm = 0.78 x 760 mm = 592.8 mm
Concentration in solutionKH x PN2 = 8.42 x 10-7 M (mm)-1 x 592.8 mm = 4.99 x 10-4 M
CUET Exam Question No: 7
The solubility of N2 in water at 300 K and 500 torr partial pressure is 0.01 g L-1) at 750 torr partial pressure is
Option A : 0.02
Option B : 0.015
Option C : 0.0075
Option D : 0.005
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 0.015
According to Henry’s law, p1/ p2 = S1/ S2
[p1 and p2 are partial pressures and S1 and S2 are solubilities]
⇒ 500/ 750 = 0.01/ S2 ⇒ S2 = 750 x 0.01 / 500 = 0.015 g L-1
CUET Chemistry Practice Questions No: 8
When a binary solution of two volatile liquids is taken in a closed vessel, then
Option A : Both the components would evaporate and an equilibrium would be established between vapour phase and liquid phase
Option B : Both the components would evaporate but equilibrium would not be established between vapour phase and liquid phase
Option C : None of components would evaporate and no equilibrium would be established between vapour phase and liquid phase
Option D : None of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: Both the components would evaporate and an equilibrium would be established between vapour phase and liquid phase
When a binary solution of two volatile liquids is taken in a closed vessel, then both the components get evaporated and finally a state of equilibrium is established between the vapour and liquid phase. The total pressure in this case is the sum of the partial pressure of each component.
CUET Chemistry Sample Paper Question No: 9
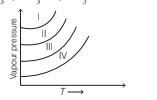
The following diagram shows the vapor pressure curves for CH3, f , CH3, OH, CH3, COOH and HCHO. Curves I, II, III and IV respectively are
Option A : CH3F; HCHO; CH3OH; CH3 COOH
Option B : CH3 COOH; CH3OH; CH3F; HCHO
Option C : HCHO; CH3F; CH3OH; CH3 COOH
Option D : CH3OH; CH3COOH; HCHO; CH3F
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: CH3F; HCHO; CH3OH; CH3 COOH
The vapour pressure increases with decrease in intermolecular interactions. Moreover, lesser the intermolecular forces, more is the volatility and, hence higher vapour pressure at a given temperature.
CUET Chemistry Mock Test Question No: 10
Raoult’s law becomes a special case of Henry’s law, when
Option A : Ku = pi°
Option B : Ku > pi°
Option C : Ku < pi°
Option D : Ku > pi°
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: Ku = pi°
According to Raoult’s law, the vapour pressure of a volatile component in a given solution is pi = pi° χi
If in the solution of a gas in liquid, the volatile component exists as a gas, then according to Henry’s law, p = KHχ
Therefore, Raoult’s law becomes a special case of Henry’s law when KH becomes equal to pi° .
CUET Chemistry Question No: 11
At 300 K two pure liquids A and B have 150 mm Hg and 100 mm Hg vapour pressures, respectively. In an equimolar liquid mixture of A and B, the mole fraction of B in the vapour mixture at this temperature is
Option A : 0.6
Option B : 0.5
Option C : 0.8
Option D : 0.4
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: 0.4
CUET Exam Chemistry Question No: 12
The vapour pressure of pure CHCl3 and CH2 Cl 2are 200 and 41.5 atm respectively. The weight of CHCl3 and CHCl2 2 are respectively 11.9 g and 17 g. The vapour pressure of solution will be
Option A : 80.5 atm
Option B : 79.5 atm
Option C : 94.3 atm
Option D : 105.5 atm
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 94.3 atm
Given Vapour Pressure of pure CH3CI [p1] and CH2 CI2 [p2] = 200 atm and 41.5 atm respectively. Weight (w1) of CH2 CI and CH2 CI2 (w2) = 11.9 w g and 17g respectively. Molar mass of CHCl3 CHCl3(M1) and CH2Cl2(M2) =119 g mol−1 and 85 g mol−1 respectively. Thus, number of moles (n) of CH3Cl = 119/ 119 = 0.01 mol
Number of moles of CH2Cl2= 17/ 85 = 0.2 mol
ptotal = p1 X1 + P2 X2
X1 = n1 / nr = 0.1 / 0.3 = 0.33
X2 = n2 / n3 = 0.2 / 0.3 = 0.66
ptotal = 200 x 0.33 + 4.15 x 0.66 = 94.3 atm
CUET UG Chemistry Question No: 13
For an ideal solution, the correct option is
Option A : ∆mix V ≠ 0 at constant T and p
Option B : ∆mix H = 0 at constant T and p
Option C : ∆mix G = 0 at constant T and p
Option D : ∆mix S = 0 at constant T and p
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: ∆mix H = 0 at constant T and p
Ideal solutions are those which obey Raoult’s law over all concentration ranges at a given temperature, e.g. benzene-toluene, n-hexane-n-heptane, etc. For an ideal solution, ∆Vmix = 0, ∆Hmix = 0, ∆Gmix < 0, ∆Smix > 0
CUET Domain Subject Chemistry Question No: 14
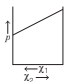
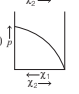
For a binary ideal liquid solution, the variation in total vapour pressure versus composition of solution is given by which of the curves?
Option A :
Option B :
Option C :
Option D : Both (a) and (b)
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: Both (a) and (b)
Depending on the vapour pressures of the pure components 1 and 2, total vapour pressure over the solution decreases or increases with the increase of the mole fraction of component 1. Thus, the variation in total vapour pressure versus composition of solution is given by then curves given in option (a) and (b).
CUET BSc Chemistry Question No: 15
The solution which show large positive deviation from Raoult’s law form
Option A : maximum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition.
Option B : maximum freezing azeotrope at a specific composition.
Option C : minimum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition.
Option D : minimum freezing azeotrope at a specific composition.
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: minimum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition.
The solution which shows large positive deviation from Raoult’s law forms minimum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition. e.g. ether-acetone, ethanol-water etc.
CUET Entrance Exam Chemistry Question No: 16
The examples of minimum boiling azeotropes are
Option A : aniline + acetone
Option B : acetic acid + pyridine
Option C : HCl + water
Option D : cyclohexane + ethanol
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: cyclohexane + ethanol
In cyclohexane and ethanol, the intermolecular interactions are weaker than those between cyclohexane-cyclohexane and ethanol-ethanol. Therefore, shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law and hence forms minimum boiling azeotropes.
CUET Exam Question No: 17
The solution that forms maximum boiling azeotrope is
Option A : carbon disulphide − acetone
Option B : benzene − toluene
Option C : acetone − chloroform
Option D : n-hexane − n-heptane
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: acetone − chloroform
Solution which show negative deviation from Raoult’s law are called maximum boiling azeotrope. Hence, acetone and chloroform forms maximum boiling azeotrope.
CUET Chemistry Practice Questions No: 18
Relative lowering of vapour pressure is a colligative property because
Option A : it depends on the concentration of a non-electrolyte solute in solution and does not depend on the nature of the solute molecules
Option B : it depends on number of particles of electrolytic solute in solution as well as on the nature of the solute particles
Option C : it depends on the concentration of a non-electrolyte solute in solution as well as on the nature of the solute molecules
Option D : it depends on the concentration of an electrolyte or non-electrolyte solute in solution as well as on the nature of solute molecules
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: it depends on the concentration of a non-electrolyte solute in solution and does not depend on the nature of the solute molecules
Relative lowering of vapour pressure is a colligative property because
(i) it does not depend upon nature of solute.
(ii) it depends upon number of solute particles.
(iii) it depends upon concentration of non-electrolyte solution.
CUET Chemistry Sample Paper Question No: 19
At room temperature, a dilute solution of urea is prepared by dissolving 0.60 g of urea in 360 g of water. If the vapour pressure of pure water at this temperature is 35 mm Hg, lowering of vapour pressure will be (Molar mass of urea = 60 g mol −1)
Option A : 0.027 mm Hg
Option B : 0.031 mm Hg
Option C : 0.017 mm Hg
Option D : 0.028 mm Hg
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 0.017 mm Hg
CUET Chemistry Mock Test Question No: 20
The van’t Hoff factor (i) for a compound which undergoes dissociation in one solvent and association in other solvent is respectively
Option A : greater than one and greater than one
Option B : less than one and greater than one
Option C : less than one and less than one
Option D : greater than one and less than one
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: greater than one and less than one
In case of dissociation, van’t Hoff factor i > 1and in case of association, van’t Hoff factor i < 1.