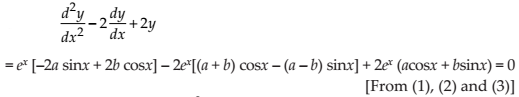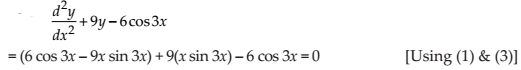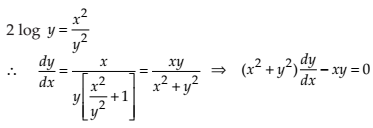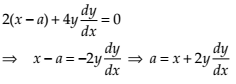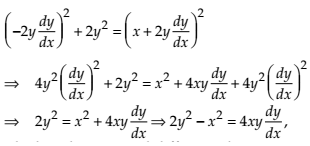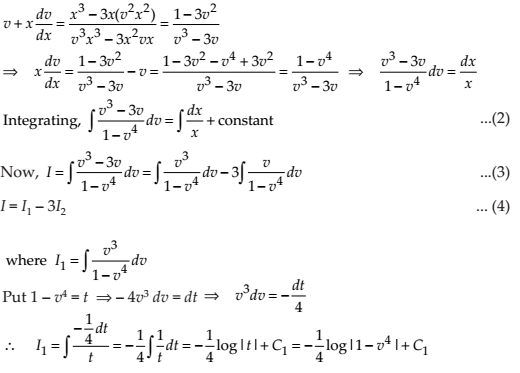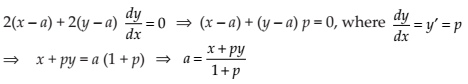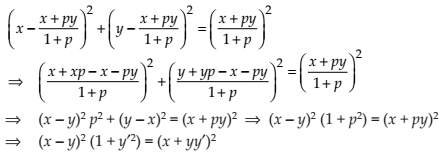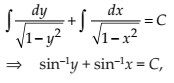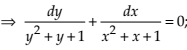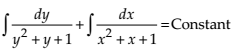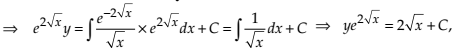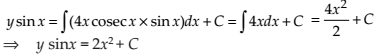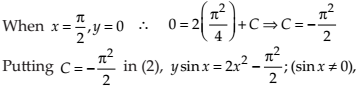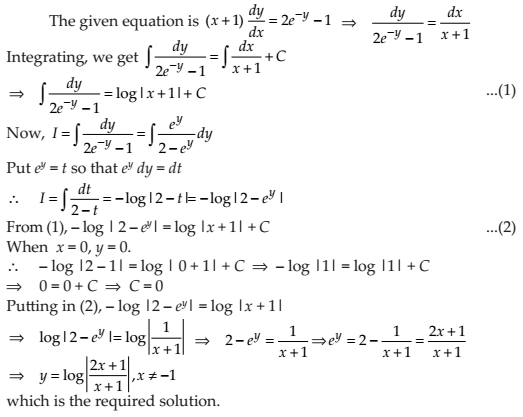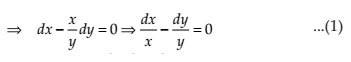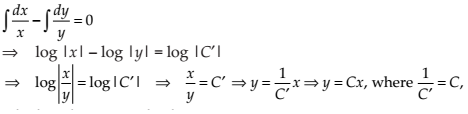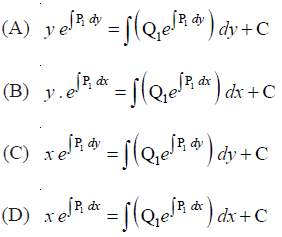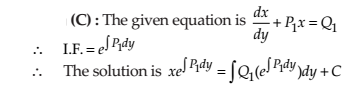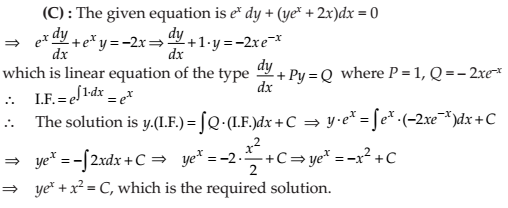NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise
Hi Students, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMB). In this post, you will get the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise.
CBSE Class 12th is an important school class in your life as you take some serious decision about your career. And out of all subjects, Maths is an important and core subjects. So CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 12th Maths is major role in your exam preparation as it has detailed chapter wise solutions for all exercise. This NCERT Solutions can be downloaded in PDF file. The downloading link is given at last.
NCERT Solutions for class 12 is highly recommended by the experienced teacher for students who are going to appear in CBSE Class 12 and JEE Mains and Advanced and NEET level exams. Here You will get NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise of all questions given in NCERT textbooks of class 12 in details with step by step process.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths are not only the solutions of Maths exercise but it builds your foundation of other important subjects. Getting knowledge of depth concept of CBSE Class 12th Maths like Algebra, Calculus, Trigonometry, Coordinate Geometry help you to understand the concept of Physics and Physical Chemistry.
As we know that all the schools affiliated from CBSE follow the NCERT books for all subjects. You can check the CBSE NCERT Syllabus. Thus, NCERT Solutions helps the students to solve the exercise questions as given in NCERT Books.
The PDF books of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 are the first step towards the learning and understanding the each sections of Maths, Physics, Chemistry, Biology as it all help in engineering medical entrance exams. To solve it, you just need to click on download links of NCERT solutions for class 12.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 1
For each of the differential equations given below, indicate its order and degree (if defined).
(i)
NCERT Solutions:
Given differential equation is 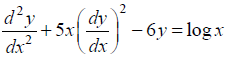
The highest order derivative present in the given differential equation is , so its order is TWO.
The given differential equation is a polynomial equation in its derivatives and the highest power of the derivative is one. So, its degree is ONE.
(ii)
NCERT Solutions:
Given differential equation is 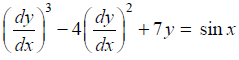
The highest order derivative present in the given differential equation is , so its order is ONE.
The given differential equation is a polynomial equation in its derivatives and the highest power of the derivative 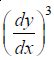
(iii)
NCERT Solutions:
Given differential equation is 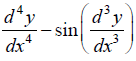
The highest order derivative present in the given differential equation is , so its order is FOUR.
The given differential equation is not a polynomial equation in its derivatives and so its degree is NOT Defined.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 2
For each of the exercises given below, verify that the given function (implicit or explicit) is a solution of the corresponding differential equation.
(i) Check whether the function y = aex + be–x + x2 is the solution of .
NCERT Solutions:
Given function is y = aex + be–x + x2 …(1)
Differentiating the equation (1) with respect to x, we get
…(2)
Differentiating the equation (2) with respect to x, we get
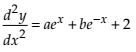
Now,
Thus, the given function y = aex + be–x + x2 is NOT the solution of .
(ii) Check whether the function y = ex (a cos x + b sin x) is the solution of 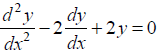
NCERT Solutions:
Given function is y = ex(a cos x + b sin x) …(1)
Differentiating the equation (1) with respect to x, we get
…(2)
Differentiating the equation (2) with respect to x, we get
…(3)
Now,
Thus, the given function y = ex (a cos x + b sin x) is the solution of 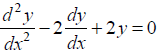
(iii) Check whether the function y = x sin 3x is the solution of 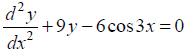
NCERT Solutions:
Given function is y = x sin 3x …(1)
Differentiating the equation (1) with respect to x, we get
…(2)
Differentiating the equation (2) with respect to x, we get
…(3)
Now,
Thus, the given function y = x sin 3x is the solution of 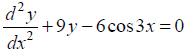
(iv) Check whether the function x2 = 2y2 log y is the solution of 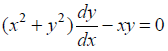
NCERT Solutions:
Given function is x2 = 2y2 log y …(1)
Differentiating the equation (1) with respect to x, we get
…(2)
From (1),
Thus, the given function x2 = 2y2 log y is the solution of 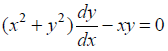
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 3
Form the differential equation representing the family of curves given by (x – a)2 + 2y2 = a2, where a is an arbitrary constant.
NCERT Solutions:
Given equation is (x – a)2 + 2y2 = a2 …(1)
Differentiating (1) with respect to x, we get
Putting in (1), we get
Thus, the differential equation of the given equation is .
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 4
Prove that x2 – y2 = c (x2 + y2)2 is the general solution of differential equation (x3 – 3xy2) dx = (y3 – 3x2y) dy, where c is a parameter.
NCERT Solutions:
Given differential equation is
…(1)
In equation (1), we see that dy/dx is in form of g(y/x), so it is a Homogeneous function of degree zero. Thus, the given differential equation is Homogeneous Differential Equation.
To solve this, we need to put y = vx …(2)
Differentiating the equation (2) with respect to x, we get
On substituting y = vx and in equation (1), we get
On squaring both sides, we get x2 – y2 = c(x2 + y2)2 where c = C’2 is an arbitrary constant.
Thus, x2 – y2 = c(x2 + y2)2 is the general solution of the given differential equation.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 5
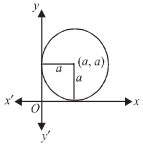
Form the differential equation of the family of circles in the first quadrant which touch the coordinate axes.
NCERT Solutions:
Let the equation of the family of the circles which touch the co-ordinates axes in the first quadrant is
(x – a)2 + (y – a)2 = a2 …(1)
, where a is the radius of the circle.
Differentiating (1) with respect to x, we get
Substituting the value of ‘a’ in (1), we get
This is required differential equation of the family of circles in the first quadrant which touch the coordinate axes.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 6
Find the general solution of the differential equation 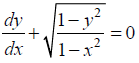
NCERT Solutions:
Given differential equation is
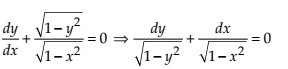
Integrating both sides, we get
This is required general solution of the given differential equation.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 7
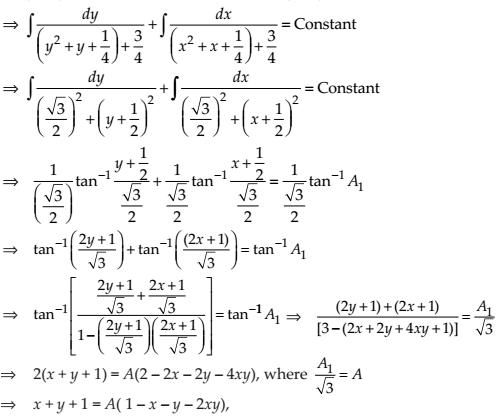
Show that the general solution of the differential equation 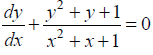
NCERT Solutions:
Given differential equation is 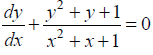
Integrating both sides, we get
Thus, the general solution of the given differential equation is (x + y + 1) = A (1 – x – y – 2xy).
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 8
Find the equation of the curve passing through the point 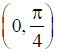
NCERT Solutions:
Given differential equation is sin x cos y dx + cos x sin y dy = 0.
Integrating both sides, we get
⇒ –log |cos x| – log|cos y| = –log|C|
⇒ –log |cos x cos y| = –log|C|
⇒ cos x cos y = C
Since the curve passes through 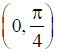
Thus,
This is required equation of the given curve.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 9
Find the particular solution of the differential equation (1 + e2x) dy + (1 + y2) ex dx = 0, given that y = 1 when x = 0.
NCERT Solutions:
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 10
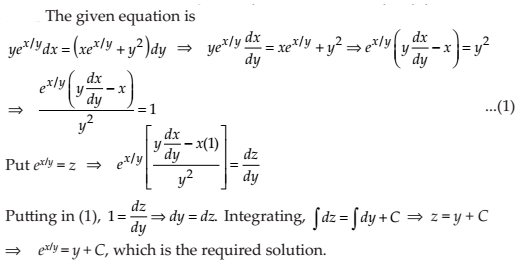
Solve the differential equation .
NCERT Solutions:
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 11
Find a particular solution of the differential equation (x – y) (dx + dy) = dx – dy, given that y = –1, when x = 0. (Hint: put x – y = t)
NCERT Solutions:
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 12
Solve the differential equation 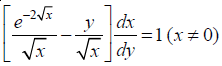
NCERT Solutions:
Given differential equation is 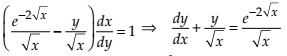
This equation is a type of 
.
Now, the Integrating Factor (IF) is .
Thus, the solution of the given differential equation is .
Putting the values of IF and Q, we get
This is required general solution of the given differential equation.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 13
Find a particular solution of the differential equation 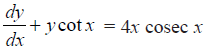
NCERT Solutions:
Given differential equation is 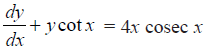
This equation is a type of 
Now, the Integrating Factor (IF) is .
Thus, the solution of the given differential equation is .
Putting the values of IF and Q, we get
This is required particular solution of the given differential equation.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 14
Find a particular solution of the differential equation (x + 1)(dy/dx) = 2 e–y – 1, given that y = 0 when x = 0.
NCERT Solutions:
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 15
The population of a village increases continuously at the rate proportional to the number of its inhabitants present at any time. If the population of the village was 20, 000 in 1999 and 25000 in the year 2004, what will be the population of the village in 2009?
NCERT Solutions:
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 16
The general solution of the differential equation 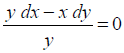
(A) xy = C
(B) x = Cy2
(C) y = Cx
(D) y = Cx2
NCERT Solutions:
Given differential equation is 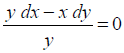
Integrating both sides, we get
This is required general solution.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 17
The general solution of a differential equation of the type 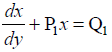
NCERT Solutions:
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Math Differential Equations Miscellaneous Exercise Ques No 18
The general solution of the differential equation ex dy + (yex + 2x) dx = 0 is
(A) x ey + x2 = C
(B) x ey + y2 = C
(C) y ex + x2 = C
(D) y ey + x2 = C
NCERT Solutions: