SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 1
The length of the diagonal BD of the parallelogram ABCD is 18 cm. If P and Q are the centroid of ∆ABC and ∆ABC respectively, length of PQ is
Options:
A. 4 cm
B. 12 cm
C. 6 cm
D. 9 cm
Answer: C
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 2
In rhombus ABCD, a straight line through C cuts extended AD at P and extended AD at P and extended AB at Q. If DP = (1/2)AB, then the ratio of BQ : AB is
Options:
A. 1 : 2
B. 2 : 1
C. 3 : 1
D. 1 : 1
Answer: B
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 3
ABCD is a trapezium whose side AD is parallel to BC. Diagonals AC and BD intersect at O. If AO = 3, CO = x – 3, BO = 3x – 19 and DO = x – 5, the values of x will be
Options:
A. 7, 10
B. 7, 6
C. 12, 6
D. 8 : 9
Answer: B
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 4
Inside a square ABCD, the triangle BCE is an equilateral triangle. If CE and BD intersect at O, then the value of the angle BOC is
Options:
A. 75 degrees
B. 60 degrees
C. 90 degrees
D. 120 degrees
Answer: A
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 5
The side AB of a parallelogram ABCD is extended to E such that BE = AB and DE intersects BC at Q. Then the point Q divides BC in the ratio
Options:
A. 1 : 2
B. 2 : 1
C. 1 : 1
D. 2 : 3
Answer: C
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 6
ABCD is a rhombus whose side AB = 4 cm and angle ABC = 120 degrees. Then the length of the diagonal BD is
Options:
A. 4 cm
B. 2 cm
C. 1 cm
D. 3 cm
Answer: A
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 7
In a rhombus ABCD, AB is produced to F and BA is produced to E such that AB = AE = BF. Then
Options:
A. ED ⊥ CF
B. ED > CF
C. ED2 + CF2 = EF2
D. ED || CF
Answer: A
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 8
In a quadrilateral ABCD with unequal sides if the diagonals AC and BD intersect at right angles then
Options:
A. AB2 + BC2 = 2(CD2 + DA2)
B. AB2 + BC2 = CD2 + DA2
C. AB2 + CD2 = BC2 + DA2
D. AB2 + AD2 = BC2 + CD2
Answer: C
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 9
If P and Q are two points on sides AB and AD of a parallelogram ABCD respectively and areas of ∆CPD = A1 and that of ∆BQC = A2, then
Options:
A. 2A1 = A2
B. A1 = A2
C. A1 = 2A2
D. 2A1 = 3A2
Answer: B
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 10
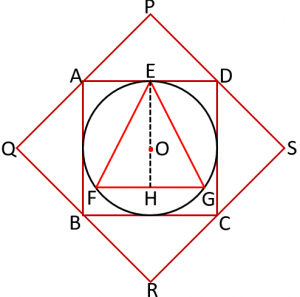
In the following figure, a square ABCD is formed with its vertices as the mid-points of a larger square PQRS. A circle is inscribed in square ABCD and ∆EFG is an equilateral triangle inscribed in the circle. If the length of side of square PQRS is a, then the area of ∆EFG is
Options:
A. √3 a2/16
B. 3√3 a2/32
C. 5√3 a2/32
D. 5√3 a2/64
Answer: B
Solution:
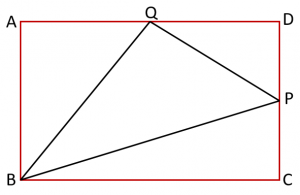
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 11
In the figure below, P and Q are the mid-points of two sides CD and AD of a rectangle ABCD respectively. The ratio of the areas ∆BPQ and the rectangle ABCD is
Options:
A. 4 : 9
B. 5 : 8
C. 8 : 13
D. 3 : 8
Answer: D
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 12
In a quadrilateral ABCD, ∠B = 90 degrees and AD2 = AB2 + BC2 + CD2, then ∠ACD is
Options:
A. 45 degrees
B. 60 degrees
C. 50 degrees
D. 90 degrees
Answer: D
Solution:
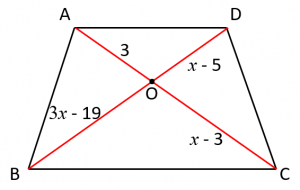
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 13
In the figure below, the lengths of the four sections of the two diagonals of a trapezium ABCD namely AO, BO, CO and DO are given. Then, find the possible values of x.
Options:
A. 6, 8
B. 8, 9
C. 9, 7
D. 7, 8
Answer: B
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 14
If the ratio of the angles of a quadrilateral is 2 : 7 : 2 : 7, then the shape of the quadrilateral is
Options:
A. is a rhombus
B. is a parallelogram
C. is a trapezium
D. cannot be identified
Answer: D
Solution:
SSC CGL Geometry Quadrilateral Set 1 : Ques No 15
If D, E and F are the mid-points of sides BC, CA and AB respectively of ∆ABC, then the ratio of the area of the parallelogram DEFB to the area of the trapezium CAFD is
Options:
A. 2 : 3
B. 3 : 4
C. 1 : 3
D. 1 : 2
Answer: A
Solution: