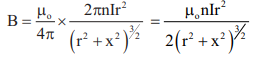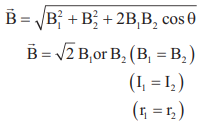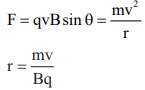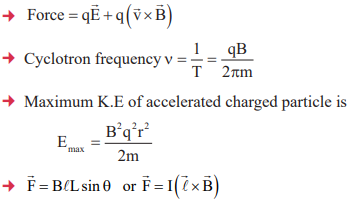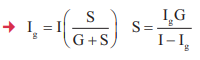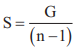Hi CUET aspirants, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMBIPi). In this post, you will get CUET Physics Study Materials Moving Charges and Magnetism Notes AMBIPi. This CUET Physics Notes are designed by analyzing to the CUET Syllabus and CUET Previous Years Questions Papers.
CUET Physics Notes
CUET Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism: Important Points to Remember
There are following important points in this chapter of Moving Charges and Magnetism.
- If the length of the solenoid is more than about five or six times of its diameter then solenoid normally taken as infinitely long.
- A linear solenoid carrying current is equivalent to a bar magnet.
- The magnetic field induction at a point just outside the curved face of the solenoid carrying current is zero.
- If a current carrying circular loop (n = 1) is turned into a coil having n identical turns, then magnetic field at the center of the coil becomes n2 of the previous field B’ = n2B0.
- Cyclotron frequency is also known as magnetic resonance frequency.
- Energy of charged particle moving in uniform magnetic field does not change because it experiences a force in perpendicular direction of motion. If magnetic field is not uniform it will change.
- Magnetic field lines can enters in the surface of any magnetic material at any angle.
- If a particle enters a magnetic field normally to the magnetic field, then it starts moving in a circular orbit.
- The point at which it enters the magnetic field lies on the circumference not on the centre of circle that it makes.
- Main function of the soft iron core in galvanometer is to make magnetic field lines radial.
- Range of ammeter can be increased by using a suitable shunt in parallel with ammeter but we can not decrease the
range of ammeter. - Range of voltameter can be decreased or increased by using suitable resistance in series or parallel with the galvanometer.
- Dead beat galvanometer is one in which the coil comes to rest at once after the passage of current through it.
- Nature of magnetic field is radial in galvanometer.
- A moving coil galvanometer can’t be used to detect a.c in a circuit since it measures average value of current and
average value of a.c is zero over a complete cycle. - Galvanometer can not be used as an ammeter directly because it measures limited current, gives full scale
deflection by passing only small amount of current.
CUET Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism: Important Formulas
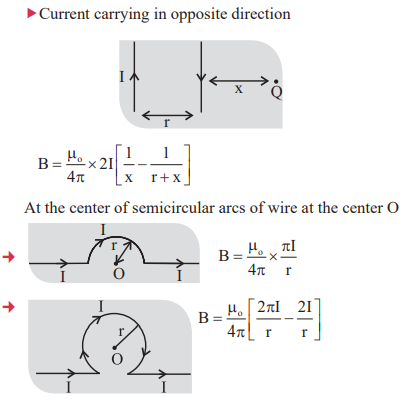
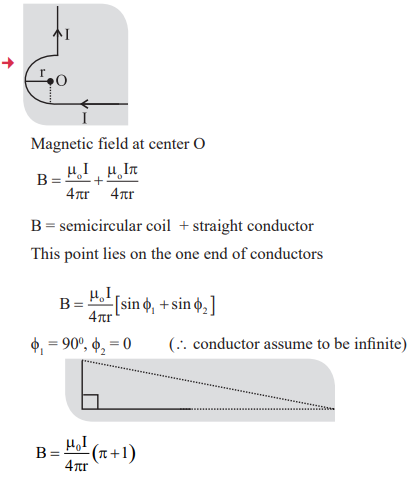
1. Magnetic field induction at a point due to current element
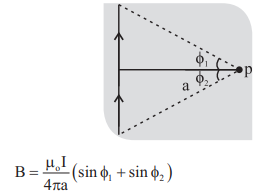
2. Magnetic field induction at a point due to linear conductor carrying current is
3. In case of long infinite conductor
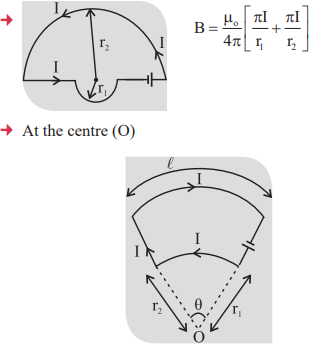
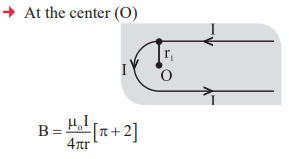
4. Magnetic field induction at the centre of circular coil.
5. Magnetic field induction at a point on the axis of the circular coil of radius (r) carrying current I is
the center of circular coil.
where x = Distance of point on the axis of circular coil from
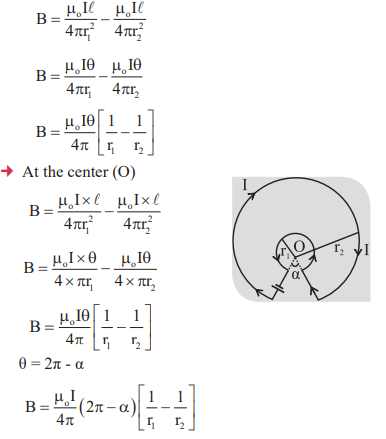
6. Ampere’s circuital law
7. Magnetic-Field
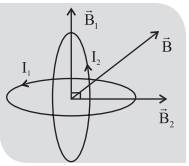
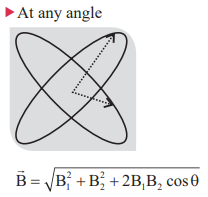
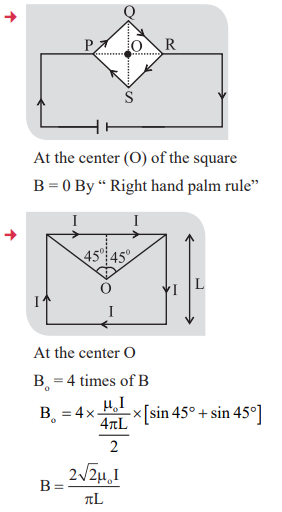
8. Resultant magnetic field due to two current carrying circular coil
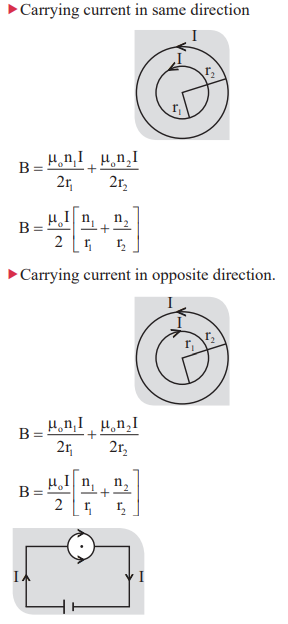
9. Magnetic field at the center of two concentric circular coils:
At the center magnetic field is zero by the “ Right hand palm rule”
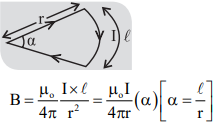
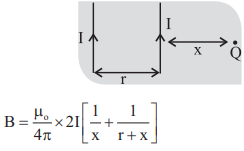
10. Magnetic field due to straight current carrying conductor.
11. Magnetic field at a point from current carrying conductors carrying current in same direction.
12. Force on charged particle of charge q in an electric field E, F = qE.
13. Force on charged particle of charge q moving with velocity ν in magnetic field B is
14. When magnetic field is acting perpendicular to the direction of motion of charged particle then
15. Time of revolution
16. Force per unit length on each of the two long parallel conductors carrying currents I1 & I2 placed distance r apart.
17. Force on smaller conductors of length ‘l‘ carrying currents I1, held parallel to infinite and small conductors carrying current I2 is
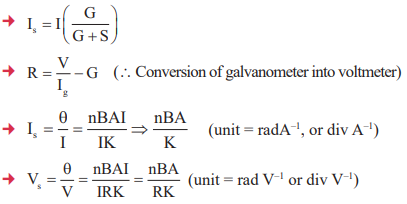
18. Sensitivity of Galvanometer and Conversion & Electric Current
19. To increase the range of voltameter n times the resistance to be connected in series R = (n – 1)G
20. To increase the range of ammeter n times the value of shunt to be connected in parallel
21. Resistance of ideal voltameter and ammeter is ∞ & zero respectively
CUET Physics Mock Test
Now, you have revised the this CUET Physics chapter. So, you must need to practice CUET Physics Sample Papers. By solving these CUET Physics questions, you will be more confident about your CUET preparations.