Hi CUET aspirants, Welcome to Amans Maths Blogs (AMBIPi). In this post, you will get CUET Chemistry Mock Test Haloalkanes Haloarenes AMBIPi. This CUET Chemistry Mock Test is of the Chemistry chapter Haloalkanes Haloarenes. Before solving these CUET Chemistry questions, you must read CUET Chemistry Notes, which helps you to revise CUET Chemistry Syllabus and then you must need to solve CUET Previous Years Questions Papers.
CUET Chemistry Mock Test
CUET Chemistry Question No: 1
Which of the following is not an allylic halide?
Option A : 5-bromo pent-1-ene
Option B : 4-bromopent-2-ene
Option C : 3-bromo-2-methylbut-1-ene
Option D : 1-bromobut-2-ene
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: 5-bromo pent-1-ene
5-bromopent-1-ene is not an allylic halide, whereas option (b), (c) and (d) are allylic halide, because in these compounds,
the halogen atom is bonded to an sp3 hybridised carbon atom adjacent to C —C double bond.
H2C — CH2 —CH2—C ≡ CH
¦ ¦
Br H
(not allylic)
CUET Exam Chemistry Question No: 2
Which of the following is an example of vic-dihalide?
Option A : Dichloromethane
Option B : 1,2-dichloroethane
Option C : Ethylidine chloride
Option D : Allyl chloride
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: 1,2-dichloroethane
1, 2-dichloroethane is an example of 1, 2-dichloro ethane. In vic-dihalide, the halogen atoms are present at adjacent C-atoms.
e.g. CH2 — CH2
¦ ¦ CI CI
1,2-dichloroethane
CUET UG Chemistry Question No: 3
The lattice points of a crystal of hydrogen iodide are occupied by
Option A : HI molecules
Option B : H atoms and I atoms
Option C : H+ cations and I− anions
Option D : H2 molecules and I2 molecules
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: HI molecules
Since, HI is a covalent molecule, so HI molecules are present at the lattice points of the crystal.
CUET Domain Subject Chemistry Question No: 4
What is the IUPAC name of the fillowing compound?
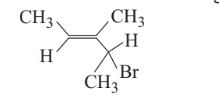
Option A : 3-bromo-3-methyl-1,2-dimethylprop-1-ene
Option B : 3-bromo-1,2-dimethybut-1-ene
Option C : 2-bromo-3-methylpent-3-ene
Option D : 4-bromo-3-methylpent-2-ene
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: 4-bromo-3-methylpent-2-ene
CUET BSc Chemistry Question No: 5
Which of the following is best for preparation of alkyl halides?
Option A : Alcohol
Option B : Alkene
Option C : Alkane
Option D : Alkyne
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: Alcohol
CUET Entrance Exam Chemistry Question No: 6
Which of the following is used to prepare alkyl chloride in presence of alcohol?
Option A : H2SO4
Option B : HCl solution (dilute)
Option C : dry HCl gas
Option D : None of these
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: dry HCl gas
Dry HCl (hydrogen chloride) gas is used to prepare alkyl chloride in presence of alcohol. In this method, dry HCl gas is passed through a solution of alcohol.
CUET Exam Question No: 7
The alkane that gives only one monochloro product on chlorination with CI2 in presence of diffused
Option A : 2, 2-dimethylbutane
Option B : neo-pentane
Option C : n-pentane
Option D : isopentane
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: neo-pentane
CUET Chemistry Practice Questions No: 8
When a primary aromatic amine dissolved in cold aqueous mineral acid (HCl) is treated with sodium nitrite, the product formed is
Option A : aryl halide
Option B : diazonium salt
Option C : 2° aromatic amine
Option D : None of these
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: diazonium salt
When a primary aromatic amine, dissolved or suspended in cold aqueous mineral acid (HCl) is treated with sodium nitrite, a diazonium salt is formed.
CUET Chemistry Sample Paper Question No: 9
Which of the following alkyl halides has maximum density?
Option A : C3H7I
Option B : C2H5I
Option C : CH3Br
Option D : CH3I
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: CH3I
CH3I has maximum density because of smallest hydrocarbon part i.e (CH3) and contian heaviest halogen (i.e. I).
CUET Chemistry Mock Test Question No: 10
Which of the following has the highest melting point but least solubility in a given solvent?
Option A : o-dichlorobenzene
Option B : p-dichlorobenzene
Option C : m-dichlorobenzene
Option D : chlorobenzene
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: p-dichlorobenzene
Due to symmetry, the molecule of p-dichlorobenzene fit closely in the lattice. As a result, intermolecular forces are strongest in p-dichlorobenzene and, hence it has highest melting point and least solubility.
CUET Chemistry Question No: 11
Which of the following reaction(s) is not given by haloalkanes?
Option A : Nucleophilic substitution reactions
Option B : Elimination reaction
Option C : Reaction with metals
Option D : Addition reactions
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: Addition reactions
Addition reactions are not given by haloalkanes, whereas nucleophilic substitution, elimination reactions and reaction with metals are given by haloalkanes.
CUET Exam Chemistry Question No: 12
What is the nature of KCN and AgCN compounds?
Option A : Ionic and covalent
Option B : Ionic and ionic
Option C : Covalent and ionic
Option D : Covalent and covalent
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: Ionic and covalent
CUET UG Chemistry Question No: 13
The correct order of reactivity of alkyl halides toward SN1is as follows.
Option A : 2° halide > 3° halide > 1° halide > CH3X
Option B : 3° halide > 1° halide > 2° halide > CH3X
Option C : 3° halide > 2° halide > 1° halide > CH3X
Option D : CH3X > 1° halide > 2° halide > 3° halide
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: CH3X > 1° halide > 2° halide > 3° halide
CUET Domain Subject Chemistry Question No: 14
The allylic and benzylic halides follow
Option A : SN1 mechanism
Option B : SN2 mechanism
Option C : Both SN1 and SN2 mechanism
Option D : None of the above
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: SN1 mechanism
CUET BSc Chemistry Question No: 15
Which of the following is correct order for the ease of dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halide with alc. KOH?
Option A : 3° < 2° < 1°
Option B : 3° > 2° < 1°
Option C : 3° > 2° > 1°
Option D : 3° < 2° > 1°
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option C: 3° > 2° > 1°
The correct order for the ease of dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halide with conc. KOH is 3° > 2° > 1°, because 3° carbocation is more stable.
CUET Entrance Exam Chemistry Question No: 16
Among the following, the suitable reagent for Wurtz reaction is
Option A : Na/alcohol
Option B : Na/ether
Option C : Zn/ether
Option D : Zn/alcohol
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: Na/ether
CUET Exam Question No: 17
When freon is manufactured by tetrachloromethane, the reaction involved in this process is called
Option A : Sandmeyer reaction
Option B : Swarts reaction
Option C : Finkelstein reaction
Option D : All of these
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: Swarts reaction
CUET Chemistry Practice Questions No: 18
Which of the following compound is used as an organic insecticide?
Option A : Chloroform
Option B : Freon-12
Option C : Carbon tetrachloride
Option D : DDT
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option D: DDT
CUET Chemistry Sample Paper Question No: 19
Consider the following reaction,
2CHCl3 + O2 → A + B
The products A and B of above reaction respectively are
Option A : CO2 and HCI
Option B : COCI2 and HCI
Option C : CO and HCI
Option D : None of these
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option B: COCI2 and HCI
CUET Chemistry Mock Test Question No: 20
Which of the following is not correct?
Option A : PhCH2Br>PhCHBrCH3>PhCBr(CH3)2(SN1)
Option B : R—I > R—Br > R—Cl (SN2)
Option C : CH2 = CH —CI < CH2= CH —CH2 —CI < PhCH2— CI (SN1)
Option D : R—Cl < R—Br < R—I (SN1)
Show/Hide Answer Key
Option A: PhCH2Br>PhCHBrCH3>PhCBr(CH3)2(SN1)
In the given crystal structure, equal number of cations and anions are missing (two K+ and two Cl–) from their normal lattice sites and the crystal maintains its electrical neutrality. Hence, this is Schottky defect.
